
Back Notch-Signalweg German Notch signaling pathway English Ruta de señalización Notch Spanish Voie de signalisation Notch French Notch-jelzőút Hungarian Jalur persinyalan Notch ID Notch Italian Notchシグナリング Japanese Significans iter NOTCH Latin Notch-signalering Dutch
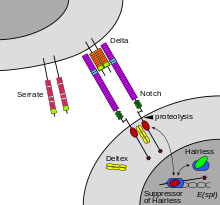
Notch receptor je transmembránový protein a receptor živočišných[1] buněk. V extracelulární části obsahuje opakující se EGF motivy, které vytváří vazebnou doménu pro vazbu Notch ligandu (např. proteinu Delta u octomilek).[2] Notch byl původně pojmenován u octomilek (Drosophila), u C. elegans se nachází dva Notch receptory (lin-12 a glp-1),[3] u člověka se gen nazývá TAN-1,[4][chybí lepší zdroj] u myši int-3[5] a u Xenopus je to Xotch.[6]
- ↑ GAZAVE, E.; LAPÉBIE, P.; RICHARDS, G. S., et al. Origin and evolution of the Notch signalling pathway: an overview from eukaryotic genomes. BMC Evol Biol.. 2009, roč. 9, s. 249. Dostupné online. ISSN 1471-2148.
- ↑ LODISH, Harvey, et al.. Molecular Cell Biology. 5. vyd. New York: W.H. Freedman and Company, 2000. Dostupné online.
- ↑ THEODOSIOU, A.; ARHONDAKIS, S.; BAUMANN, M., et al. Evolutionary scenarios of Notch proteins. Mol Biol Evol.. 2009, roč. 26, čís. 7, s. 1631–40. Dostupné online. ISSN 1537-1719.
- ↑ ELLISEN, L. W.; BIRD, J.; WEST, D. C., et al. TAN-1, the human homolog of the Drosophila notch gene, is broken by chromosomal translocations in T lymphoblastic neoplasms. Cell.. 1991, roč. 66, čís. 4, s. 649–61. Dostupné online. ISSN 0092-8674.
- ↑ ROBBINS, J.; BLONDEL, B. J.; GALLAHAN, D., et al. Mouse mammary tumor gene int-3: a member of the notch gene family transforms mammary epithelial cells. J Virol.. 1992, roč. 66, čís. 4, s. 2594–9. Dostupné online. ISSN 0022-538X.
- ↑ COFFMAN, C.; HARRIS, W.; KINTNER, C. Xotch, the Xenopus homolog of Drosophila notch. Science.. 1990, roč. 249, čís. 4975, s. 1438–41. Dostupné online. ISSN 0036-8075.