
Back Amitriptilien Afrikaans أميتربتيلين Arabic Amitriptilin Azerbaijani آمی تریپتیلین AZB Amitriptilina Catalan Amitriptylin Welsh Αμιτριπτυλίνη Greek Amitriptyline English Amitriptilina Spanish Amitriptüliin Estonian
| Strukturformel | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Allgemeines | ||||||||||||||||||||||
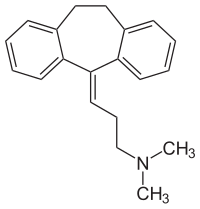
| Freiname | Amitriptylin | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Andere Namen |
3-(10,11-Dihydro-5H-dibenzo[a,d]cyclohepten-5-yliden)-N,N-dimethylpropylamin | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Summenformel |
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| Externe Identifikatoren/Datenbanken | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Arzneistoffangaben | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC-Code | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wirkstoffklasse | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wirkmechanismus |
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| Eigenschaften | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molare Masse |
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| Schmelzpunkt |
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| pKS-Wert |
9,4[2] | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Sicherheitshinweise | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxikologische Daten | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wenn nicht anders vermerkt, gelten die angegebenen Daten bei Standardbedingungen (0 °C, 1000 hPa). | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Amitriptylin ist ein Arzneistoff aus der Gruppe der trizyklischen Antidepressiva, der in erster Linie zur Behandlung von Depressionen und zur langfristigen Schmerzbehandlung eingesetzt wird. In einer Übersichtsstudie von 2001 wurde es als „Goldstandard-Antidepressivum“ bezeichnet.[4]
- ↑ a b c Datenblatt Amitriptylinhydrochlorid bei Sigma-Aldrich, abgerufen am 29. Mai 2022 (PDF).
- ↑ W. M. Haynes (Hrsg.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics. 97. Auflage. (Internet-Version: 2016), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton FL, Dissociation Constants of Organic Acids and Bases, S. 5-89.
- ↑ a b c d e f g A. Kleemann, J. Engel, B. Kutscher, D. Reichert: Pharmaceutical Substances – Synthesis, Patents, Applications. 4. Auflage. Thieme-Verlag, Stuttgart 2000, ISBN 1-58890-031-2.
- ↑ C. Barbui, M. Hotopf: Amitriptyline v. the rest: still the leading antidepressant after 40 years of randomised controlled trials. In: The British Journal of Psychiatry: The Journal of Mental Science. Band 178, Februar 2001, S. 129–144, PMID 11157426.