
Back انتخابات الرئاسة الأمريكية 1800 Arabic ھەڵبژاردنی سەرۆکایەتیی ویلایەتە یەکگرتووەکانی ئەمریکا (١٨٠٠) CKB Volby prezidenta USA 1800 Czech Præsidentvalget i USA 1800 Danish Präsidentschaftswahl in den Vereinigten Staaten 1800 German Elecciones presidenciales de Estados Unidos de 1800 Spanish انتخابات ریاستجمهوری ایالات متحده آمریکا (۱۸۰۰) Persian Yhdysvaltain presidentinvaalit 1800 Finnish Élection présidentielle américaine de 1800 French הבחירות לנשיאות ארצות הברית 1800 HE
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
138 members of the Electoral College 70 electoral votes needed to win | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 32.3%[1] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
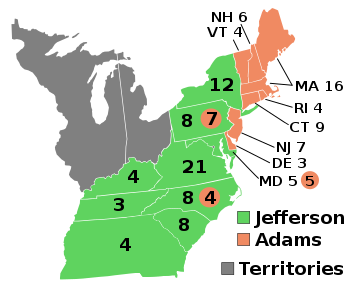 Presidential election results map. Green denotes states won by Jefferson and Light Orange denotes states won by Adams. Numbers indicate the number of electoral votes cast by each state. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1801 contingent U.S. presidential election | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
16 state delegations of the House of Representatives 9 state votes needed to win | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 1801 Contingent Election Results. Green denotes states voting for Jefferson and blue denotes states voting for Burr. States in grey cast blank ballots. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Presidential elections were held in the United States from October 31 to December 3, 1800. In what is sometimes called the "Revolution of 1800",[2] the Democratic-Republican Party candidate, Vice President Thomas Jefferson, defeated the Federalist Party candidate and incumbent, President John Adams. The election was a political realignment that ushered in a generation of Democratic-Republican leadership. This was the first presidential election in American history to be a rematch. It was also the first election in American history where an incumbent president did not win re-election.
Adams had narrowly defeated Jefferson in the 1796 election. Under the rules of the electoral system in place before the 1804 ratification of the Twelfth Amendment to the United States Constitution, each member of the Electoral College cast two votes, with no distinction made between electoral votes for president and electoral votes for vice president. As Jefferson received the second-most votes in 1796, he was elected vice president. In 1800, unlike in 1796, both parties formally nominated tickets. The Democratic-Republicans nominated a ticket consisting of Jefferson and Aaron Burr, while the Federalists nominated a ticket consisting of Adams and Charles C. Pinckney. Each party formed a plan by which one of their respective electors would vote for a third candidate or abstain so that its preferred presidential candidate (Adams for the Federalists and Jefferson for the Democratic-Republicans) would win one more vote than the party's other nominee.[citation needed]
The chief political issues revolved around the fallout from the French Revolution and the Quasi-War. The Federalists favored a strong central government and close relations with Great Britain. The Democratic-Republicans favored decentralization to the state governments, and the party attacked the taxes the Federalists imposed. The Democratic-Republicans also denounced the Alien and Sedition Acts, which the Federalists had passed to make it harder for immigrants to become citizens and to restrict statements critical of the federal government. The Democratic-Republicans were well organized at the state and local levels, while the Federalists were disorganized and suffered a bitter split between their two major leaders, Adams and Alexander Hamilton. According to historian John Ferling, the jockeying for electoral votes, regional divisions, and the propaganda smear campaigns created by both parties made the election recognizably modern.[3]
At the end of a long and bitter campaign, Jefferson and Burr each won 73 electoral votes, Adams won 65, and Pinckney won 64. The Federalists swept New England, the Democratic-Republicans dominated the South, and the parties split the Mid-Atlantic states of New York, New Jersey, and Pennsylvania.
The Democratic-Republicans' assumption that one or more electors in Rhode Island, Vermont, New Jersey, Georgia, Kentucky, or Tennessee would vote for Jefferson and not Burr[4] resulted in a tie, known as the Burr dilemma. It necessitated a contingent election in the House of Representatives. Under the terms laid out in the Constitution, the outgoing House of Representatives chose between Jefferson and Burr. Burr was accused of campaigning for the presidency himself in the contingent election despite being a member of Jefferson's party. Each state delegation cast one vote, and a victory in the contingent election required one candidate to win a majority of the state delegations. Neither Burr nor Jefferson was able to win on the first 35 ballots of the contingent election, as most Federalist representatives backed Burr and all Democratic-Republican representatives backed Jefferson. Hamilton favored Jefferson over Burr, and he convinced several Federalists to switch their support to Jefferson, giving Jefferson a victory on the 36th ballot. Jefferson became the second consecutive incumbent vice president to be elected president. This is one of two presidential elections (along with the 1824 election) that have been decided in the House.
- ^ "National General Election VEP Turnout Rates, 1789-Present". United States Election Project. CQ Press.
- ^ "Thomas Jefferson: The Revolution of 1800". PBS. Archived from the original on October 30, 2013. Retrieved April 23, 2012.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Ferling 2004was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Larson, Edward (2007). A Magnificent Catastrophe. Free Press. p. 242. ISBN 978-0-7432-9316-7.
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).



