
Back انتخابات الرئاسة الأمريكية 1836 Arabic ھەڵبژاردنی سەرۆکایەتیی ویلایەتە یەکگرتووەکانی ئەمریکا (١٨٣٦) CKB Præsidentvalget i USA 1836 Danish Präsidentschaftswahl in den Vereinigten Staaten 1836 German Elecciones presidenciales de Estados Unidos de 1836 Spanish انتخابات ریاستجمهوری ایالات متحده آمریکا (۱۸۳۶) Persian Yhdysvaltain presidentinvaalit 1836 Finnish Élection présidentielle américaine de 1836 French הבחירות לנשיאות ארצות הברית 1836 HE Elezioni presidenziali negli Stati Uniti d'America del 1836 Italian
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
294 members of the Electoral College 148 electoral votes needed to win | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 56.5%[1] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
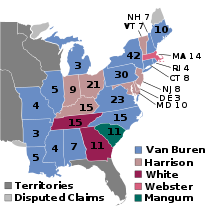 Presidential election results map. Blue denotes states won by Van Buren/Johnson, Yellow denotes those won by Harrison/Granger, Maroon denotes those won by White/Tyler, Pink denotes those won by Webster/Granger, and Green denotes those won by Mangum/Tyler. Numbers indicate the number of electoral votes allotted to each state. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1837 contingent U.S. vice presidential election | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
52 United States senators 27 votes needed to win | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Senate by state. Blue denotes states that voted for Johnson, Yellow denotes those that voted for Granger, Green denotes those that did not vote. State with multiple colors had Senators that voted differently from each other. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Presidential elections were held in the United States from November 3 to December 7, 1836. Incumbent Vice President Martin Van Buren, candidate of the Democratic Party, defeated four candidates fielded by the nascent Whig Party.
The 1835 Democratic National Convention chose a ticket of Van Buren (President Andrew Jackson's handpicked successor) and U.S. Representative Richard Mentor Johnson of Kentucky. The Whig Party, which had only recently emerged and was primarily united by opposition to Jackson, was not yet sufficiently organized to agree on a single candidate. Hoping to compel a contingent election in the House of Representatives by denying the Democrats an electoral majority, the Whigs ran multiple candidates. Most Northern and border state Whigs supported the ticket led by former Senator William Henry Harrison of Ohio, while most Southern Whigs supported the ticket led by Senator Hugh Lawson White of Tennessee. Two other Whigs, Daniel Webster and Willie Person Mangum, carried Massachusetts and South Carolina respectively on single-state tickets.
Despite facing multiple candidates, Van Buren won a majority of the electoral vote, and he won a majority of the popular vote in both the North and the South. Nonetheless, the Whig strategy came very close to success, as Van Buren won the decisive state of Pennsylvania by just over two points. As Virginia's electors voted for Van Buren but refused to vote for Johnson, Johnson fell one vote short of an electoral majority, compelling a contingent election for vice president. In that contingent election, the United States Senate elected Johnson over Harrison's running mate, Francis Granger.
Van Buren was the third incumbent vice president to win election as president, an event which would not happen again until 1988, when George H. W. Bush was elected president. He is also the most recent Democrat to be elected to succeed a two-term Democratic president, and the only sitting Democratic vice president to win the presidency.[2] This also marks the last time that a sitting vice president was elected president after only serving for one term. Harrison finished second in both the popular and electoral vote, and his strong performance helped him win the Whig nomination in the 1840 presidential election. The election of 1836 was crucial in developing the Second Party System and a stable two-party system more generally. By the end of the election, nearly every independent faction had been absorbed by either the Democrats or the Whigs.[3]
- ^ "National General Election VEP Turnout Rates, 1789-Present". United States Election Project. CQ Press.
- ^ Murse, Tom (December 16, 2020). "Last Time Consecutive Democratic Presidents Were Elected". ThoughtCo.
You'd have to go back even further in history to find the most recent instance of a Democrat being elected to succeed a two-term president from the same party. The last time that happened was in 1836 when voters elected Martin Van Buren to follow Andrew Jackson.
- ^ Cole, Donald B. (1984). Martin Van Buren and the American Political System. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. p. 279. ISBN 0-691-04715-4. Retrieved March 23, 2017.






