
Back انتخابات الرئاسة الأمريكية 1944 Arabic ھەڵبژاردنی سەرۆکایەتیی ویلایەتە یەکگرتووەکانی ئەمریکا (١٩٤٤) CKB Præsidentvalget i USA 1944 Danish Präsidentschaftswahl in den Vereinigten Staaten 1944 German Elecciones presidenciales de Estados Unidos de 1944 Spanish انتخابات ریاستجمهوری ایالات متحده آمریکا (۱۹۴۴) Persian Yhdysvaltain presidentinvaalit 1944 Finnish Élection présidentielle américaine de 1944 French הבחירות לנשיאות ארצות הברית 1944 HE ԱՄՆ նախագահական ընտրություններ 1944 Armenian
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
531 members of the Electoral College 266 electoral votes needed to win | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 55.9%[1] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
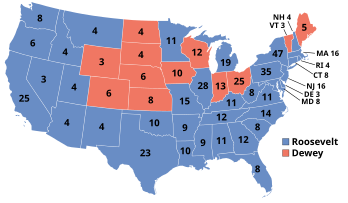 Presidential election results map. Blue denotes those won by Roosevelt/Truman, red denotes states won by Dewey/Bricker. Numbers indicate the number of electoral votes allotted to each state. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Presidential elections were held in the United States on November 7, 1944, during World War II. Incumbent Democratic President Franklin D. Roosevelt defeated Republican Thomas E. Dewey to win an unprecedented fourth term. It was also the fifth (and second consecutive) presidential election in which both major party candidates were registered in the same home state; the others have been in 1860, 1904, 1920, 1940, and 2016.
Roosevelt had become the first president to win a third term with his victory in the 1940 presidential election, with little doubt that he would seek a fourth term. Unlike in 1940, Roosevelt faced little opposition within his own party, and he easily won the presidential nomination of the 1944 Democratic National Convention. Concerned that Roosevelt's ill health would mean the vice president would likely become president, the convention dropped Roosevelt's vice president Henry A. Wallace in favor of Senator Harry S. Truman of Missouri.[2] Governor Dewey of New York emerged as the frontrunner for the Republican nomination after his victory in the Wisconsin primary, and he defeated conservative Governor John W. Bricker at the 1944 Republican National Convention.
As World War II was going well for the United States and the Allies, Roosevelt remained popular despite his long tenure. Dewey campaigned against the New Deal and for a smaller government, but was ultimately unsuccessful in convincing the country to change course. The election was closer than Roosevelt's other presidential campaigns, but Roosevelt still won by a 7.5 percentage point margin in the popular vote and by a wide margin in the Electoral College. Rumors of Roosevelt's ill health, although somewhat dispelled by his vigorous campaigning, proved to be prescient; Roosevelt died less than three months into his fourth term and was succeeded by Truman. This was the last election until 2024 in which a presidential candidate won two elections with different vice presidential candidates.
- ^ "Voter Turnout in Presidential Elections". The American Presidency Project. UC Santa Barbara.
- ^ Smith, Jean Edward (2007). FDR. New York: Random House. pp. 617–619. ISBN 978-1-4000-6121-1. OCLC 71350593.

