
Back الانتخابات الرئاسية الأمريكية 2000 Arabic ABŞ-də prezident seçkiləri (2000) Azerbaijani Президентски избори в САЩ (2000) Bulgarian Eleccions presidencials dels Estats Units del 2000 Catalan 2000 nièng Mī-guók cūng-tūng sōng-gṳ̄ CDO ھەڵبژاردنی سەرۆکایەتیی ویلایەتە یەکگرتووەکانی ئەمریکا (٢٠٠٠) CKB Volby prezidenta USA 2000 Czech Præsidentvalget i USA 2000 Danish Präsidentschaftswahl in den Vereinigten Staaten 2000 German Προεδρική εκλογή των Ηνωμένων Πολιτειών 2000 Greek
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
538 members of the Electoral College 270 electoral votes needed to win | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 54.2%[1] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
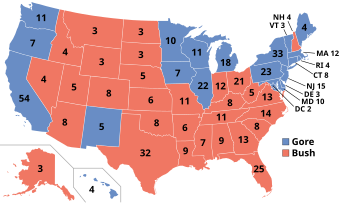 Presidential election results map. Red denotes states won by Bush/Cheney and blue denotes those won by Gore/Lieberman. One of D.C.'s three electors cast a blank ballot for president and vice president. Numbers indicate electoral votes cast by each state and the District of Columbia. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Presidential elections were held in the United States on November 7, 2000. Republican nominee Governor George W. Bush of Texas, the eldest son of 41st President George H. W. Bush, narrowly defeated incumbent Democratic Vice President Al Gore. It was the fourth of five U.S. presidential elections, and the first since 1888, in which the winning candidate lost the popular vote, and is considered one of the closest U.S. presidential elections in history, with long-standing controversy about the result.[2][3][4][5] Gore conceded the election on December 13 after the Supreme Court issued its decision.
Incumbent Democratic President Bill Clinton was ineligible to seek a third term because of term limits established by the 22nd Amendment. Incumbent Vice President Gore easily secured the Democratic nomination, defeating former New Jersey Senator Bill Bradley in the primaries. He selected Connecticut Senator Joe Lieberman as his running mate. Bush was seen as the early favorite for the Republican nomination, and after a contentious primary battle with Arizona Senator John McCain and others, he secured the nomination by Super Tuesday. He selected former Secretary of Defense Dick Cheney as his running mate.
Both major-party candidates focused primarily on domestic issues, such as the budget, tax relief, and reforms for federal social insurance programs, although foreign policy was not ignored. Due to President Clinton's sex scandal with Monica Lewinsky and subsequent impeachment, Gore avoided campaigning with Clinton. Republicans denounced Clinton's indiscretions, while Gore criticized Bush's lack of experience.


On election night, it was unclear who had won, with the electoral votes of the state of Florida still undecided. The returns showed that Bush won Florida by such a close margin that state law required a recount. A month-long series of legal battles led to the highly controversial 5–4 U.S. Supreme Court decision Bush v. Gore, which ended the recount. Ultimately, Bush won Florida by 537 votes, a margin of 0.009%. The Florida recount and subsequent litigation resulted in major post-election controversy, with some analysis suggesting that limited county-based recounts would have confirmed a Bush victory, whereas a statewide recount would have given the state to Gore.[6][7] Post-election analysis found that Palm Beach County's butterfly ballot misdirected over 2,000 votes from Gore to third-party candidate Pat Buchanan, tipping Florida—and the election—to Bush.[8]
Ultimately, Bush won 271 electoral votes, one vote more than the 270 required to win, while Gore won the popular vote by 543,895 votes (a margin of 0.52% of all votes cast).[9] Bush flipped 11 states that had voted Democratic in 1996: Arkansas, Arizona, Florida, Kentucky, Louisiana, Missouri, Nevada, New Hampshire, Ohio, Tennessee, and West Virginia. Despite Gore's loss, this election marked the first time since 1948 that the Democratic Party won the popular vote in three consecutive elections. This was the last time until 2024 in which an incumbent vice president ran for president. This was also the last time a Republican received an electoral vote from New England until 2016.
- ^ "National General Election VEP Turnout Rates, 1789-Present". United States Election Project. CQ Press. Archived from the original on July 25, 2014. Retrieved February 21, 2023.
- ^ Pruitt, Sarah. "7 Most Contentious U.S. Presidential Elections". HISTORY. Archived from the original on April 27, 2019. Retrieved September 1, 2019.
- ^ Haddad, Ken (November 7, 2016). "5 of the closest Presidential elections in US history". WDIV. Archived from the original on January 10, 2019. Retrieved September 1, 2019.
- ^ Fain, Thom. "5 of the closest presidential elections in U.S. history". fosters.com. Archived from the original on January 10, 2019. Retrieved September 1, 2019.
- ^ Wood, Richard (July 25, 2017). "Top 9 closest US presidential elections since 1945". Here Is The City. Archived from the original on January 10, 2019. Retrieved September 1, 2019.
- ^ Wolter, Kirk; Jergovic, Diana; Moore, Whitney; Murphy, Joe; O'Muircheartaigh, Colm (February 2003). "Statistical Practice: Reliability of the Uncertified Ballots in the 2000 Presidential Election in Florida" (PDF). The American Statistician. 57 (1). American Statistical Association: 1–14. doi:10.1198/0003130031144. ISSN 0003-1305. JSTOR 3087271. S2CID 120778921. Archived from the original (PDF) on March 18, 2016. Retrieved June 12, 2016.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
battlewas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "The Butterfly Did It: The Aberrant Vote for Buchanan in Palm Beach County, Florida". Stanford Graduate School of Business. Retrieved October 23, 2024.
- ^ "Federal Elections 2000: 2000 Presidential Electoral and Popular Vote Table". Federal Election Commission. Archived from the original on July 9, 2017. Retrieved March 22, 2017.
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).

