
Back Арнауҭ бызшәа Abkhazian Албаныбзэ ADY Albanees Afrikaans Albanische Sprache ALS አልባንኛ Amharic Idioma albanés AN Albanisc sprǣc ANG अल्बेनियाई भाषा ANP اللغة الألبانية Arabic ܠܫܢܐ ܐܠܒܢܝܐ ARC
| Albanian | |
|---|---|
| Shqip Arbërisht | |
| Pronunciation | [ʃcip] ⓘ [ˈɟuha ˈʃcipɛ] [aɾbəˈɾiʃt] |
| Native to | |
| Ethnicity | Albanians |
Native speakers | 7.5 million (2017)[1][2] |
Indo-European
| |
Early forms | |
| Dialects |
|
| Official status | |
Official language in |
|
Recognised minority language in | |
| Regulated by | Academy of Sciences of Albania Academy of Sciences and Arts of Kosovo |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | sq |
| ISO 639-2 | alb (B) sqi (T) |
| ISO 639-3 | sqi – inclusive codeIndividual codes: aae – Arbëreshaat – Arvanitikaaln – Ghegals – Tosk |
| Glottolog | alba1267 |
| Linguasphere | to 55-AAA-ahe (25 varieties) 55-AAA-aaa to 55-AAA-ahe (25 varieties) |
 | |
Albanian (endonym: shqip [ʃcip] ⓘ, gjuha shqipe [ˈɟuha ˈʃcipɛ], or arbërisht [aɾbəˈɾiʃt]) is an Indo-European language and the only surviving representative of the Albanoid branch, which belongs to the Paleo-Balkan group.[9] It is the native language of the Albanian people. Standard Albanian is the official language of Albania and Kosovo, and a co-official language in North Macedonia and Montenegro, where it is the primary language of significant Albanian minority communities. Albanian is recognized as a minority language in Italy, Croatia, Romania, and Serbia. It is also spoken in Greece and by the Albanian diaspora, which is generally concentrated in the Americas, Europe and Oceania.[2][10] Albanian is estimated to have as many as 7.5 million native speakers.[1][2]
Albanian and other Paleo-Balkan languages had their formative core in the Balkans after the Indo-European migrations in the region.[11][12] Albanian in antiquity is often thought to have been an Illyrian language for obvious geographic and historical reasons,[13][14][15][16][17][18] or otherwise an unmentioned Balkan Indo-European language that was closely related to Illyrian and Messapic.[19][20][21][22] The Indo-European subfamily that gave rise to Albanian is called Albanoid in reference to a specific ethnolinguistically pertinent and historically compact language group.[23] Whether descendants or sisters of what was called 'Illyrian' by classical sources, Albanian and Messapic, on the basis of shared features and innovations, are grouped together in a common branch in the current phylogenetic classification of the Indo-European language family.[24][19][23][21][22]
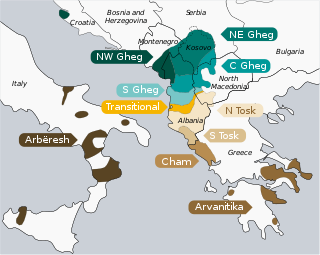
The first written mention of Albanian was in 1284 in a witness testimony from the Republic of Ragusa, while a letter written by Dominican Friar Gulielmus Adea in 1332 mentions the Albanians using the Latin alphabet in their writings. The oldest surviving attestation of modern Albanian is from 1462.[25] The two main Albanian dialect groups (or varieties), Gheg and Tosk, are primarily distinguished by phonological differences and are mutually intelligible in their standard varieties,[26][27] with Gheg spoken to the north and Tosk spoken to the south of the Shkumbin river.[28] Their characteristics[29][30] in the treatment of both native words and loanwords provide evidence that the split into the northern and the southern dialects occurred after Christianisation of the region (4th century AD),[31][32] and most likely not later than the 6th century AD,[33][34][35] hence possibly occupying roughly their present area divided by the Shkumbin river since the Post-Roman and Pre-Slavic period, straddling the Jireček Line.[36][37]
Centuries-old communities speaking Albanian dialects can be found scattered in Greece (the Arvanites and some communities in Epirus, Western Macedonia and Western Thrace),[38] Croatia (the Arbanasi), Italy (the Arbëreshë)[39] as well as in Romania, Turkey and Ukraine.[40] The Malsia e Madhe Gheg Albanian[41][42] and two varieties of the Tosk dialect, Arvanitika in Greece and Arbëresh in southern Italy, have preserved archaic elements of the language.[43] Ethnic Albanians constitute a large diaspora, with many having long assimilated in different cultures and communities. Consequently, Albanian-speakers do not correspond to the total ethnic Albanian population, as many ethnic Albanians may identify as Albanian but are unable to speak the language.[44][45][46]
Standard Albanian is a standardised form of spoken Albanian based on Tosk.
- ^ a b Rusakov 2017, p. 552.
- ^ a b c Cite error: The named reference
KlBrFr1800was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "Language and alphabet Article 13". Constitution of Montenegro. WIPO. 19 October 2007.
Serbian, Bosnian, Albanian and Croatian shall also be in the official use.
- ^ Franceschini 2014, pp. 533–534 [1]
- ^ "Application of the Charter in Serbia" (PDF). European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. 11 June 2013. pp. 4–5, 9.
- ^ Franceschini, Rita (2014). "Italy and the Italian-Speaking Regions". In Fäcke, Christiane (ed.). Manual of Language Acquisition. Walter de Gruyter GmbH. p. 546. ISBN 9783110394146.
- ^ "Reservations and Declarations for Treaty No.148 – European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages". Council of Europe. Archived from the original on 8 December 2015. Retrieved 3 December 2015.
- ^ Coretta, Stefano; Riverin-Coutlée, Josiane; Kapia, Enkeleida; Nichols, Stephen (2022). "Northern Tosk Albanian". Journal of the International Phonetic Association. 53 (3). Illustration of the IPA: 1–23. doi:10.1017/S0025100322000044. hdl:20.500.11820/ebce2ea3-f955-4fa5-9178-e1626fbae15f.
- ^ Orel 2000, p. 12; Matzinger 2018, p. 1790; Matasović 2019, p. 39; Hamp 1963, p. 104; Katicic 2012, p. 184: "And yet we know that it is the continuation of a language spoken in the Balkans already in ancient times. This has been proved by the fact that there are Ancient Greek loan words in Albanian".
- ^ Fatjona Mejdini (3 May 2013). "Albania Aims to Register its Huge Diaspora". Balkan Insight. Retrieved 17 January 2017.
- ^ Friedman, Victor (2022). "The Balkans". In Salikoko Mufwene, Anna Maria Escobar (ed.). The Cambridge Handbook of Language Contact: Volume 1: Population Movement and Language Change. Cambridge Handbooks in Language and Linguistics. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9781009115773.
- ^ Lazaridis, Iosif; Alpaslan-Roodenberg, Songül; et al. (26 August 2022). "The genetic history of the Southern Arc: A bridge between West Asia and Europe". Science. 377 (6609): eabm4247. doi:10.1126/science.abm4247. PMC 10064553. PMID 36007055. S2CID 251843620.
- ^ Coretta, Stefano; Riverin-Coutlée, Josiane; Kapia, Enkeleida; Nichols, Stephen (16 August 2022). "Northern Tosk Albanian". Journal of the International Phonetic Association. 53 (3): 1122–1144. doi:10.1017/S0025100322000044. hdl:20.500.11820/ebce2ea3-f955-4fa5-9178-e1626fbae15f.
Though the origin of the language has been debated, the prevailing opinion in the literature is that it is a descendant of Illyrian (Hetzer 1995).
- ^ Matasović 2019, p. 5: "Much has been written about the origin of the Albanian language. The most probable predecessor of Albanian was Illyrian, since much of the present-day Albania was inhabited by the Illyrians during the Antiquity, but the comparison of the two languages is impossible because almost nothing is known about Illyrian, despite the fact that two handbooks of that language have been published (by Hans Krahe and Anton Mayer)... examination of personal names and toponyms from Illyricum shows that several onomastic areas can be distinguished, and these onomastic areas just might correspond to different languages spoken in ancient Illyricum. If Illyrians actually spoke several different languages, the question arises -from which 'Illyrian' language did Albanian develop, and that question cannot be answered until new data are discovered. The single "Illyrian" gloss preserved in Greek (rhínon 'fog') may have the reflex in Alb. (Gheg) re͂ 'cloud' (Tosk re)< PAlb. *ren-."
- ^ Beekes 2011, p. 25: "It is often thought (for obvious geographic reasons) that Albanian descends from ancient Illyrian (see above), but this cannot be ascertained as we know next to nothing about Illyrian itself."
- ^ Fortson 2010, p. 446: "Albanian forms its own separate branch of Indo-European; it is the last branch to appear in written records. This is one of the reasons why its origins are shrouded in mystery and controversy. The widespread assertion that it is the modern–day descendant of Illyrian, spoken in much the same region during classical times ([...]), makes geographic and historical sense but is linguistically untestable since we know so little about Illyrian."
- ^ Mallory & Adams 1997, p. 11: "Although there are some lexical items that appear to be shared between Romanian (and by extension Dacian) and Albanian, by far the strongest connections can be argued between Albanian and Illyrian. The latter was at least attested in what is historically regarded as Albanian territory and there is no evidence of any major migration into Albanian territory since our records of Illyrian occupation. The loan words from Greek and Latin date back to before the Christian era and suggest that the ancestors of the Albanians must have occupied Albania by then to have absorbed such loans from their histori-cal neighbors. As the Illyrians occupied Albanian territory at this time, they are the most likely recipients of such loans."
- ^ Villar, Francisco (1996). Los indoeuropeos y los orígenes de Europa (in Spanish). Madrid: Gredos. pp. 313–314, 316. ISBN 84-249-1787-1.
- ^ a b Friedman 2020, p. 388.
- ^ Matzinger 2018, p. 1790.
- ^ a b Ismajli 2015, p. 45.
- ^ a b Hamp & Adams 2013, p. 8.
- ^ a b Trumper 2018, p. 385.
- ^ Hyllested & Joseph 2022, p. 235.
- ^ Matasović 2019, p. 39.
- ^ Demiraj & Esposito 2009, p. 23:
"...these innovations, as those that are also evident in different varieties of Gheg, are not such as to impede communication between speakers of the two dialects. Furthermore, the major part of the Albanian lexicon is common to the two dialects."
- ^ Fortson 2010, p. 446: "The two dialects are mutually intelligible in their standard varieties, although numerous subdialects exist that show considerable variation, especially in the north and northeast of the Geg–speaking area."
- ^ Demiraj & Esposito 2009, p. 23:
"The river Shkumbin in central Albania historically forms the boundary between those two dialects, with the population on the north speaking varieties of Geg and the population on the south varieties of Tosk."
- ^ Demiraj 2006, p. 102:
"It is the case of the evolution of stressed /a-/ and partly stressed /e-/ in front of a nasal consonant to /ë-/ in thee southern dialect. While the evolution /a-/ > /ë/ in front of a nasal consonant has involved the southern dialect, the evolution /e-/ > /-ë/ in the same phonetic conditions has not taken place in the northern part and partly in the eastern part of that dialect (...). This phonetic phenomenon has appeared earlier than rhotacism, as it is clearly evidenced in such examples as llanë > llërë, ranë > rërë etc., in which the evolution /a-/ > /ë-/ could not take place before /-r-/. Since this phonetic change has not appeared in the Slavic loanwords of Albanian, but has involved mainly the I.E. inherited words as well as the loans from Old Greek (compare mokënë > mokërë < mākhanāʼ etc.) and from Latin (compare ranë > rërë > arena etc.), it has generally been acknowledged that it has taken place in the pre-Slavic period of Albanian. Its sporadic appearance in a very reduced number of Slavic loanwords is due to the action of analogy with similar cases of inherited or more ancient loans of Albanian."
- ^ Demiraj & Esposito 2009, p. 23:
"In Tosk /a/ before a nasal has become a central vowel (shwa), and intervocalic /n/ has become /r/. These two sound changes have affected only the pre-Slav stratum of the Albanian lexicon, that is the native words and loanwords from Greek and Latin."
- ^ Douglas Q. Adams (January 1997). Encyclopedia of Indo-European Culture. Taylor & Francis. pp. 9, 11. ISBN 978-1-884964-98-5.
The Greek and Latin loans have undergone most of the far-reaching phonological changes which have so altered the shape of inherited IE words while Slavic and Turkish words do not show these changes. Thus Albanian must have acquired much of its present form by the time Slavs entered into the Balkans in the fifth and sixth centuries AD [middle of p. 11] [...] The loan words from Greek and Latin date back to before the Christian era [p. 9] [...] Even very common words such as mik ʻfriendʼ (< Lat amicus) or këndoj ʻI sing; readʼ (< Lat cantāre) come from Latin and attest to a widespread intermingling of pre-Albanian and Balkan Latin speakers during the Roman period, roughly from the second century BC to the fifth century AD. [before middle of p. 11]
- ^ Fortson 2010, p. 448: "The dialectal split into Geg and Tosk happened sometime after the region became Christianized in the fourth century AD: Christian Latin loanwords show Tosk rhotacism, such as Tosk murgu 'monk' (Geg mungu) from Lat. monachus."
- ^ Demiraj 2010, pp. 77–78
- ^ Rusakov 2017, p. 559.
- ^ Demiraj 2006, pp. 102–103:
"...such sporadic analogical cases do not reverse the generally acknowledged conclusion that this dialectal peculiarity as a phonetic process has appeared in pre-Slavic period of Albanian and is relatively more ancient than the rhotacism. It has most probably appeared not later than the V-VI centuries A.D."
- ^ See also Hamp 1963 The isogloss is clear in all dialects I have studied, which embrace nearly all types possible. It must be relatively old, that is, dating back into the post-Roman first millennium. As a guess, it seems possible that this isogloss reflects a spread of the speech area, after the settlement of the Albanians in roughly their present location, so that the speech area straddled the Jireček Line.
- ^ Demiraj 2006, p. 103:
"And, as it was pointed out in §3, since the dialectal differentiations have appeared in a certain geographical area, one is entitled to draw the conclusion that the speakers of the northern and southern dialects have been present in their actual areas in the Post-Roman and Pre-Slavic period of Albanian."
- ^ Euromosaic project (2006). "L'arvanite/albanais en Grèce" (in French). Brussels: European Commission. Retrieved 5 December 2016.
- ^ "Albanians in Italy". Archived from the original on 21 January 2012. Retrieved 2 January 2012.
- ^ "Robert Elsie". The Albanian Language. 25 November 1972. Retrieved 17 January 2017.
- ^ Dedvukaj, Lindon; Ndoci, Rexhina (2023). "Linguistic variation within the Northwestern Gheg Albanian dialect". Proceedings of the Linguistic Society of America. 8 (1). Linguistic Society of America: 5501. doi:10.3765/plsa.v8i1.5501.
- ^ Dedvukaj, Lindon; Gehringer, Patrick (2023). "Morphological and phonological origins of Albanian nasals and its parallels with other laws". Proceedings of the Linguistic Society of America. 8 (1). Linguistic Society of America: 5508. doi:10.3765/plsa.v8i1.5508.
- ^ Demiraj & Esposito 2009, p. 23.
- ^ Mai, Nicola. "The Albanian diaspora-in-the-making: media, migration and social exclusion." Journal of Ethnic and Migration Studies 31, no. 3 (2005): 543–561.
- ^ de Rapper, Gilles. "Albanians facing the Ottoman past: the case of the Albanian diaspora in Turkey." (2005).
- ^ Gkaintartzi, Anastasia, Aspasia Chatzidaki, and Roula Tsokalidou. "Albanian parents and the Greek educational context: Who is willing to fight for the home language?." International Multilingual Research Journal 8, no. 4 (2014): 291–308.
Cite error: There are <ref group=note> tags on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=note}} template (see the help page).