
Back Alias (Unix) Czech Alias (kommando) Danish Alias (Unix) German Alias (Unix) Spanish Alias Persian Alias (POSIX) French Alias (פקודה) HE Alias Croatian Alias (Unix) Italian Alias (コマンド) Japanese
This article needs additional citations for verification. (July 2013) |
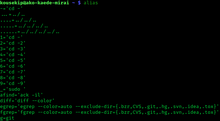 Example of alias command | |
| Original author(s) | Bill Joy |
|---|---|
| Developer(s) | Various open-source and commercial developers |
| Operating system | Unix, Unix-like, AmigaDOS, FreeDOS, Microsoft Windows, ReactOS, AROS, KolibriOS, IBM i |
| Platform | Cross-platform |
| Type | Command |
In computing, alias is a command in various command-line interpreters (shells), which enables a replacement of a word by another string.[1] It is mainly used for abbreviating a system command, or for adding default arguments to a regularly used command. alias is available in Unix shells, AmigaDOS, 4DOS/4NT, FreeDOS, KolibriOS, Windows PowerShell, ReactOS, and the EFI shell.[2] Aliasing functionality in the MS-DOS and Microsoft Windows operating systems is provided by the DOSKey command-line utility.
An alias will last for the life of the shell session. Regularly used aliases can be set from the shell's rc file (such as .bashrc) so that they will be available upon the start of the corresponding shell session. The alias commands may either be written in the config file directly or sourced from a separate file.
- ^ Rugheimer, Hannes (2020-06-10). AmigaDOS quick reference : Rügheimer, Hannes : Free Download, Borrow, and Streaming : Internet Archive. ISBN 9781557550491. Retrieved 2020-09-12 – via Internet Archive.
- ^ "EFI Shells and Scripting". Intel. Retrieved 2013-09-25.