Back Арцкі заліў Byelorussian Арцкая затока BE-X-OLD Амбракийски залив Bulgarian Golf d'Ambràcia Catalan Amvrakikós Kólpos CEB Ambrakijský záliv Czech Ambraciske Golf Danish Ambrakischer Golf German Αμβρακικός κόλπος Greek Golfo de Arta Spanish
| Ambracian Gulf | |
|---|---|
| Αμβρακικός κόλπος (Greek) | |
 | |
| Coordinates | 38°58′21″N 20°58′09″E / 38.97250°N 20.96917°E |
| Type | gulf |
| Part of | Ionian Sea (Mediterranean) |
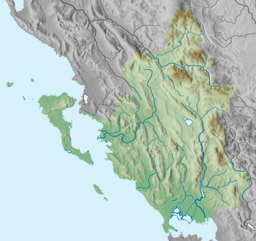
| Primary inflows | Arachthos |
| Basin countries | Greece |
| Surface area | 654 km2 (253 sq mi) |
| Average depth | 22 m (72 ft) |
| Max. depth | 60 m (200 ft) |
| Shore length1 | 40 km (25 mi) |
| Official name | Amvrakikos gulf |
| Designated | 21 August 1975 |
| Reference no. | 61[1] |
| 1 Shore length is not a well-defined measure. | |
The Ambracian Gulf, also known as the Gulf of Arta or the Gulf of Actium, and in some official documents as the Amvrakikos Gulf (Greek: Αμβρακικός κόλπος, romanized: Amvrakikos kolpos), is a gulf of the Ionian Sea in northwestern Greece. About 40 km (25 mi) long and 15 km (9 mi) wide, it is one of the largest enclosed gulfs in Greece, and due to its ecological importance is one of the National Parks of Greece. The towns of Preveza, Amphilochia (formerly Karvassaras), and Vonitsa lie on its shores.
- ^ "Amvrakikos gulf". Ramsar Sites Information Service. Retrieved 25 April 2018.