
Back Амур (псыхъо) ADY Amoer Afrikaans Amur ALS نهر آمور Arabic لواد د آمور ARY نهر امور ARZ Ríu Amur AST Amur çayı Azerbaijani آمور چایی AZB Амур Bashkir
| Amur Heilong | |
|---|---|
 | |
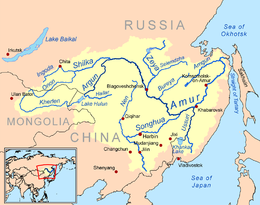 Map of the Amur watershed | |
 | |
| Etymology | From Mongolian: amar ("rest") |
| Location | |
| Countries | |
| Cities | |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | Onon-Shilka |
| • location | Khan Khentii Strictly Protected Area, Khentii Province, Mongolia |
| • coordinates | 48°48′59″N 108°46′13″E / 48.81639°N 108.77028°E |
| • elevation | 2,045 m (6,709 ft) |
| 2nd source | Argun |
| • location | Greater Khingan, Hulunbuir, China |
| • coordinates | 49°56′13″N 122°27′54″E / 49.937°N 122.465°E |
| Source confluence | |
| • location | Near Pokrovka, Russia |
| • coordinates | 53°19′58″N 121°28′37″E / 53.33278°N 121.47694°E |
| • elevation | 303 m (994 ft) |
| Mouth | Strait of Tartary |
• location | Near Nikolayevsk-on-Amur, Khabarovsk Krai, Russia |
• coordinates | 52°56′50″N 141°05′02″E / 52.94722°N 141.08389°E |
• elevation | 0 m (0 ft) |
| Length | 2,824 km (1,755 mi)[1][2] (Amur–Argun–Hailar: 4,444 km)[2] |
| Basin size | 1,855,000 km2 (716,000 sq mi)[1] 2,129,700 km2 (822,300 sq mi)(with undrained areas)[2] |
| Width | |
| • maximum | 5,000 m (16,000 ft) |
| Depth | |
| • maximum | 57 m (187 ft) |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Near mouth |
| • average | (Period: 2002–2020)12,360 m3/s (390 km3/a)[3]
(Period: 1896–2004)11,330 m3/s (400,000 cu ft/s)[4] [2] |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Bogorodskoye |
| • average | (Period: 2008–2019)11,459 m3/s (404,700 cu ft/s)[5]
(Period: 1896–2004)10,100 m3/s (360,000 cu ft/s)[4] [6] |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Komsomolsk-on-Amur |
| • average | (Period: 2012–2019)10,259 m3/s (362,300 cu ft/s)[5] |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Khabarovsk |
| • average | (Period: 2008–2018)8,384 m3/s (296,100 cu ft/s)[5]
(Period: 1896–2004)8,360 m3/s (295,000 cu ft/s)[4] |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Blagoveshchensk |
| • average | (Period: 1971–2000)2,859.1 m3/s (100,970 cu ft/s)[7] |
| Basin features | |
| Progression | Strait of Tartary (Sea of Okhotsk) |
| River system | Amur River |
| Tributaries | |
| • left | Shilka, Amazar, Oldoy, Zeya, Bureya, Arkhara, Bidzhan, Bira, Tunguska, Bolon, Gorin, Bichi, Amgun, Palvinskaya |
| • right | Argun, Emuer, Huma, Xun, Kuerbin, Songhua, Nongjiang, Ussuri, Sita, Nemta, Anyuy, Gur, Yai |
| Amur | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Russian name | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Russian | река Амур | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chinese name | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 黑龙江 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 黑龍江 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Postal | Heilung Kiang | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Literal meaning | "Black Dragon River" | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Manchu name | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Manchu script | ᠰᠠᡥᠠᠯᡳᠶᠠᠨ ᡠᠯᠠ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Romanization | Sahaliyan ula | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Amur summary route map | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Note: Distances are in kilometers. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Amur River (Russian: река Амур) or Heilong River (Chinese: 黑龙江)[8] is a perennial river in Northeast Asia, forming the natural border between the Russian Far East and Northeast China (historically the Outer and Inner Manchuria). The Amur proper is 2,824 km (1,755 mi) long, and has a drainage basin of 1,855,000 km2 (716,000 sq mi).[1][9] If including its main stem tributary, the Argun, the Amur is 4,444 km (2,761 mi) long,[9][2] making it the world's tenth longest river.
The Amur is an important river for the aquatic fauna of Northeast Asia. The river basin is home to a variety of large predatory fish such as northern snakehead, Amur pike, taimen, Amur catfish, predatory carp and yellowcheek,[10] as well as several species of trout and anadromous salmonids. The largest fish species in the Amur is the kaluga, a sturgeon that is one of the largest freshwater fish in the world, attaining a length as great as 5.6 m (18 ft).[11] It is also home to the northernmost populations of the Amur softshell turtle[12] and Indian lotus.[13]
- ^ a b c Muranov, Aleksandr Pavlovich; Greer, Charles E.; Owen, Lewis. "Amur River". Encyclopædia Britannica (online ed.). Archived from the original on 2016-05-21. Retrieved 2016-08-31.
- ^ a b c d e Eugene A., Simonov; Thomas D., Dahmer (2008). Amur-Heilong River Basin Reader (PDF). Ecosystems. ISBN 9789881722713.
- ^ Andrey, Andreev (2023). "Intra-Seasonal Variability of Sea Level on the Southwestern Bering Sea Shelf and Its Impact on the East Kamchatka and East Sakhalin Currents". Remote Sensing. 15 (20): 4984. Bibcode:2023RemS...15.4984A. doi:10.3390/rs15204984.
- ^ a b c "DRAINAGE BASINS OF THE SEA OF OKHOTSK AND SEA OF JAPAN" (PDF). pp. 60–67.
- ^ a b c Peter, Bauer-Gottwein; Elena, Zakharova; Monica, Coppo Frías; Heidi, Ranndal; Karina, Nielsen; Linda, Christoffersen (2023). "A hydraulic model of the Amur River informed by ICESat-2 elevation". Hydrological. 68 (14): 2027-2041. Bibcode:2023HydSJ..68.2027B. doi:10.1080/02626667.2023.2245811.
- ^ "Variations of the Present-Day Annual and Seasonal Runoff in the Far East and Siberia with the Use of Regional Hydrological and Global Climate Models" (PDF).
- ^ "Heilong Jiang-Amur".
- ^ Liaoning province's archive, Manchu Veritable Record Upper Vol《滿洲實錄上函/manju-i yargiyan kooli dergi dobton》
- ^ a b Амур (река в Азии), Great Soviet Encyclopedia
- ^ FishBase: Species in Amur. Archived 2019-02-18 at the Wayback Machine Retrieved 17 February 2019.
- ^ C. Michael Hogan. 2012. Amur River. Encyclopedia of Earth. Archived November 30, 2012, at the Wayback Machine Topic ed. Peter Saundry
- ^ Farkas, B., T. Ziegler, C.T. Pham, A.V. Ong and U. Fritz (2019). A new species of Pelodiscus from northeastern Indochina (Testudines, Trionychidae). ZooKeys 824: 71-86. doi:10.3897/zookeys.824.31376
- ^ Yi Zhang; Xu Lu; Shaoxiao Zeng; Xuhui Huang; Zebin Guo; Yafeng Zheng; Yuting Tian; Baodong Zheng (2015). "Nutritional composition, physiological functions and processing of lotus (Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn.) seeds: a review". Phytochem Rev. 14 (3): 321–334. doi:10.1007/s11101-015-9401-9