
Back شجرة الحياة (تشريح) Arabic Árbol de la vida (anatomía) Spanish درخت زندگی (کالبدشناسی) Persian Дрво живота (анатомија) Serbian
| Arbor vitae | |
|---|---|
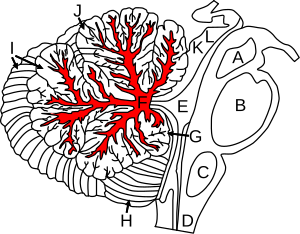 Figure shows cerebellum and surrounding regions; sagittal view of one hemisphere. A: Midbrain. B: Pons. C: Medulla. D: Spinal cord. E: Fourth ventricle. F: Arbor vitae. G: Flocculus. H: Tonsil. I: Posterior lobe. J: Anterior lobe. K: Inferior colliculus. L: Superior colliculus. | |
 Animation of the left half of the human brain. Arbor vitae is illustrated in white. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | arbor vitae cerebelli |
| NeuroNames | 692 |
| NeuroLex ID | nlx_anat_20090101 |
| TA98 | A14.1.07.401 |
| TA2 | 5789 |
| FMA | 72541 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The arbor vitae /ˌɑːrbɔːr ˈvaɪtiː/ (Latin for "tree of life") is the cerebellar white matter, so called for its branched, tree-like appearance. In some ways it more resembles a fern and is present in both cerebellar hemispheres.[1] It brings sensory and motor information to and from the cerebellum. The arbor vitae is located deep in the cerebellum. Situated within the arbor vitae are the deep cerebellar nuclei; the dentate, globose, emboliform and the fastigial nuclei. These four different structures lead to the efferent projections of the cerebellum.[2]
- ^ Saladin, Keneth (2012). Anatomy and Physiology: The Unity of Form and Function. New York, NY: McGraw Hill. p. 526. ISBN 978-0-07-337825-1.
- ^ Sodicoff, Marvin. "Cerebellum: Anatomy". Neuroanatomy Lab Resource Appendices. Temple University. Archived from the original on 20 April 2012. Retrieved 11 December 2012.