
Back Aroemeens Afrikaans Idioma arrumano AN اللغة الأرومونية Arabic Macedorrumanu AST Aromun dili Azerbaijani آرومان دیلی AZB Арамунская мова Byelorussian Арамунская мова BE-X-OLD Арумънски език Bulgarian Aroumaneg Breton
| Aromanian | |
|---|---|
| Vlach Macedo-Romanian | |
| limba armãneascã, limba armãnã, armãneashti, armãneashte, armãneashci, armãneashce, limba rãmãneascã, limba rãmãnã, rrãmãneshti | |
| Native to | Greece, Albania, North Macedonia, Bulgaria, Romania, Serbia |
| Region | Balkans |
| Ethnicity | Aromanians |
Native speakers | 210,000 (2018)[1] |
Early forms | |
| Dialects |
|
| Latin (Aromanian alphabet) | |
| Manually coded Aromanian | |
| Official status | |
Recognised minority language in | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-2 | rup |
| ISO 639-3 | rup |
| Glottolog | arom1237 |
| ELP | Aromanian |
| Linguasphere | 51-AAD-ba |
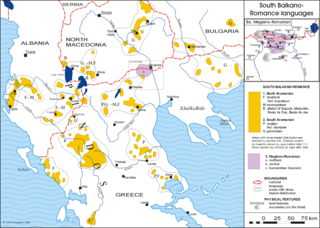 Distribution and dialects of the Aromanian language in the southwestern Balkans | |
 Aromanian is classified as Definitely Endangered by UNESCO Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger | |
| Part of a series on |
| Aromanians |
|---|
 |
| Eastern Romance languages |
|---|
|
Vulgar Latin language Substratum Thraco-Roman culture |
| Romanian |
|
| Aromanian |
| Megleno-Romanian |
| Istro-Romanian |
The Aromanian language (Aromanian: limba armãneascã, limba armãnã, armãneashti, armãneashte, armãneashci, armãneashce or limba rãmãneascã, limba rãmãnã, rrãmãneshti), also known as Vlach or Macedo-Romanian, is an Eastern Romance language, similar to Megleno-Romanian, Istro-Romanian and Romanian,[4] spoken in Southeastern Europe. Its speakers are called Aromanians or Vlachs (a broader term and an exonym in widespread use to define Romance communities in the Balkans).
Aromanian shares many features with modern Romanian, including similar morphology and syntax, as well as a large common vocabulary inherited from Latin. They are considered to have developed from Common Romanian, a common stage of all the Eastern Romance varieties.[2][a] An important source of dissimilarity between Romanian and Aromanian is the adstratum languages (external influences); whereas Romanian has been influenced to a greater extent by the Slavic languages, Aromanian has been more influenced by Greek, with which it has been in close contact throughout its history.[7]
- ^ Aromanian at Ethnologue (25th ed., 2022)

- ^ a b c Isac, Daniela (2024). Definiteness in Balkan Romance. Oxford Studies in Theoretical Linguistics. Oxford University Press. p. 1. ISBN 9780198865704.
The term 'Balkan Romance' is used to designate a group of languages including Romanian, Aromanian, Istro-Romanian and Megleno-Romanian.1 Even though the exact historical links between these languages are still unclear (...), it is commonly accepted that they have a common ancestor and hence form a coherent family. 1 Alternative names for Balkan Romance are Daco-Romance and Eastern Romance.
- ^ Dindelegan, Gabriela Pană; Maiden, Martin, eds. (2013). The Grammar of Romanian. Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780199644926.
- ^ "Romanian Language". britannica.com. Archived from the original on 2008-07-26. Retrieved 2018-05-17.
- ^ Petrucci 1999, p. 4.
- ^ Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin; Bank, Sebastian (2023-07-10). "Glottolog 4.8 – Eastern Romance". Glottolog. Leipzig: Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology. doi:10.5281/zenodo.7398962. Retrieved 2023-11-20.
- ^ Ntasiou, Evegenia (2017). Communities in Control:Learning tools and strategies for multilingualendangered language communities. Foundation for Endangered Languages. p. 71. ISBN 978-0-9560210-9-0.
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).