Back آسکاریدول AZB Ascaridol Catalan Ascaridol German Ascaridol Spanish آسکاریدول Persian Ascaridole French アスカリドール Japanese Ascaridol Portuguese Ascaridol Romanian Аскаридол Russian
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
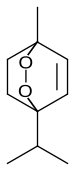
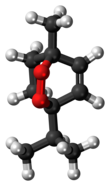
1-Methyl-4-(1-methylethyl)-2,3-dioxabicyclo[2.2.2]oct-5-ene
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| 121382 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.408 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties[1] | |||
| C10H16O2 | |||
| Molar mass | 168.23 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | Colorless liquid | ||
| Density | 1.010 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | 3.3 °C (37.9 °F; 276.4 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 40 °C (104 °F; 313 K) at 0.2 mmHg | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
 
| |||
| Danger | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Ascaridole is a natural organic compound classified as a bicyclic monoterpenoid that has an unusual bridging peroxide functional group. It is a colorless liquid with a pungent smell and taste that is soluble in most organic solvents. Like other low molecular weight organic peroxides, it is unstable and prone to rapid decomposition when heated or treated with organic acids. Ascaridole determines the specific flavor of the Chilean tree boldo and is a major constituent of the oil of Mexican tea (wormseed). It is a component of natural medicine, tonic drinks and food flavoring in Latin American cuisine. As part of the oil, ascaridole is used as an anthelmintic drug that expels parasitic worms from plants, domestic animals, and the human body.
- ^ Lewis, R. J.; Lewis, R. J. Sr (2008). Hazardous Chemicals Desk Reference. Wiley-Interscience. p. 114. ISBN 978-0-470-18024-2.