
Back توقيت أطلنطي موحد Arabic আটলান্টিক সময় অঞ্চল Bengali/Bangla Tiempo del Atlántico Spanish Waktu Standar Atlantik ID 大西洋標準時 Japanese 대서양 표준시 Korean Атлантски часовен појас Macedonian Zon Masa Atlantik Malay Atlantic Standard Time Dutch Atlantic Standard Time NN
| Atlantic Time Zone | |
|---|---|
| Time zone | |
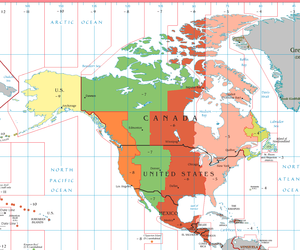 Atlantic Time Zone | |
| UTC offset | |
| AST | UTC−04:00 |
| ADT | UTC−03:00 |
| Current time | |
| 16:32, 27 January 2025 AST [refresh] | |
| Observance of DST | |
| DST is observed in parts of this time zone. | |
The Atlantic Time Zone is a geographical region that keeps standard time—called Atlantic Standard Time (AST)—by subtracting four hours from Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), resulting in UTC−04:00. AST is observed in parts of North America including several Caribbean islands. During part of the year, some portions of the zone observe daylight saving time, referred to as Atlantic Daylight Time (ADT), by moving their clocks forward one hour to UTC−03:00. The clock time in this zone is based on the mean solar time of the 60th meridian west of the Greenwich Observatory.
In Canada, the provinces of New Brunswick,[1] Nova Scotia,[2] and Prince Edward Island are in this zone, though legally they calculate time specifically as an offset of four hours from Greenwich Mean Time (GMT–4) rather than from UTC. Small portions of Quebec (eastern Côte-Nord and the Magdalen Islands) also observe Atlantic Time. Officially, the entirety of Newfoundland and Labrador observes Newfoundland Standard Time,[3] but in practice Atlantic Time is used in most of Labrador.
No part of the continental United States uses Atlantic Time, although it is used by the territories of Puerto Rico and the U.S. Virgin Islands. In the 2010s, several U.S. states considered legislation to move from the Eastern Time Zone to Atlantic Standard Time. Any changes must be approved by the United States Department of Transportation and the United States Congress before taking effect.
The United States National Hurricane Center's official advisories typically report AST and UTC when tracking storms in the Caribbean that threaten the U.S., which may confuse the mainland public not familiar with the time zone designation (although AST is equivalent to Eastern Daylight Time (EDT) for most of the Atlantic hurricane season).[4]
- ^ "CHAPTER T-6 – Time Definition Act" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2008-12-07. Retrieved 2012-09-11.
- ^ "Time Definition Act". Archived from the original on 5 June 2008. Retrieved 2008-06-02.
- ^ "RSNL1990 CHAPTER S-23 – STANDARD TIME ACT". Retrieved 2007-11-16.
- ^ "Advisories". National Hurricane Center.