
Back باريونيكسيات Arabic ব্যারিওনিচিনে Bengali/Bangla Baryonychinae Italian バリオニクス亜科 Japanese Baryonychinae Dutch Barionyksy Polish Baryonychinae Portuguese Baryonychinae Swedish
| Baryonychines Temporal range: Early Cretaceous, Possible Santonian record
| |
|---|---|
| |
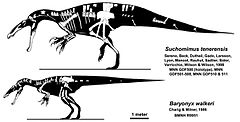
| Skeletal diagram of genera Suchomimus and Baryonyx | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Clade: | Dinosauria |
| Clade: | Saurischia |
| Clade: | Theropoda |
| Family: | †Spinosauridae |
| Subfamily: | †Baryonychinae Charig & Milner, 1986 |
| Type species | |
| †Baryonyx walkeri Charig & Milner, 1986
| |
| Subgroups | |
| |
Baryonychinae is an extinct clade or subfamily of spinosaurids from the Early Cretaceous (Valanginian-Albian) of Britain, Portugal, and Niger. The clade was named by Charig & Milner in 1986 and defined by Sereno et al. in 1998 and Holtz et al. in 2004 as all taxa more closely related to Baryonyx walkeri than to Spinosaurus aegyptiacus.[1]
Baryonychines were large, bipedal predators with elongated, crocodile-like skulls and lower jaw tips fanning out into rosettes bearing conical, often unserrated, teeth, and a distinct premaxillary notch. They possessed robust forelimbs supporting three-fingered hands with an enlarged first digit claw, to which the subfamily name indirectly refers. Members of this group, unlike the more derived Spinosaurinae, sported only low sails or none at all.
- ^ Holtz, Thomas R.; Molnar, Ralph E.; Currie, Philip J. (2019). "Basal Tetanurae". In Weishampel, David B.; Dodson, Peter; Osmólska, Halszka (eds.). The Dinosauria, Second Edition. pp. 71–110. doi:10.1525/9780520941434-009. ISBN 978-0-520-94143-4. S2CID 226816827.