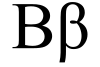Second letter of the Greek alphabet
For the German eszett, see
ß. For the Chinese radical, see
阝. For the Malayalam script, see
ദ. For other uses, see
Beta (disambiguation).
Beta (, ; uppercase Β, lowercase β, or cursive ϐ; Ancient Greek: βῆτα, romanized: bē̂ta or Greek: βήτα, romanized: víta) is the second letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of 2. In Ancient Greek, beta represented the voiced bilabial plosive IPA: [b]. In Modern Greek, it represents the voiced labiodental fricative IPA: [v] while IPA: [b] in borrowed words is instead commonly transcribed as μπ.[1][2] Letters that arose from beta include the Roman letter ⟨B⟩ and the Cyrillic letters ⟨Б⟩ and ⟨В⟩.