Back Bismut Afrikaans ቢስመዝ Amharic Bismuto AN बिस्मथ ANP بزموت Arabic بيسموث ARY بزموت ARZ Bismutu AST Bismut Azerbaijani Висмут Bashkir
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bismuth | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˈbɪzməθ/ | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | lustrous brownish silver | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Standard atomic weight Ar°(Bi) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bismuth in the periodic table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic number (Z) | 83 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Group | group 15 (pnictogens) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Period | period 6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Block | p-block | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electron configuration | [Xe] 4f14 5d10 6s2 6p3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrons per shell | 2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phase at STP | solid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point | 544.7 K (271.5 °C, 520.7 °F) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Boiling point | 1837 K (1564 °C, 2847 °F) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density (at 20° C) | 9.807 g/cm3 [3] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| when liquid (at m.p.) | 10.05 g/cm3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of fusion | 11.30 kJ/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of vaporization | 179 kJ/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar heat capacity | 25.52 J/(mol·K) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vapor pressure
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Oxidation states | common: +3 −3,[4] −2,? −1,? 0,[5] +1,? +2,? +4,? +5[4] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electronegativity | Pauling scale: 2.02 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ionization energies |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic radius | empirical: 156 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Covalent radius | 148±4 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Van der Waals radius | 207 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Natural occurrence | primordial | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Crystal structure | rhombohedral (hR2) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
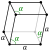
| Lattice constants | a = 0.47458 nm α = 57.236° ah = 0.45462 nm ch = 1.18617 nm (at 20 °C)[3] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal expansion | 13.09×10−6/K (at 20 °C)[a] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal conductivity | 7.97 W/(m⋅K) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrical resistivity | 1.29 µΩ⋅m (at 20 °C) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Magnetic ordering | diamagnetic | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar magnetic susceptibility | −280.1×10−6 cm3/mol[6] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Young's modulus | 32 GPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shear modulus | 12 GPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bulk modulus | 31 GPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Speed of sound thin rod | 1790 m/s (at 20 °C) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Poisson ratio | 0.33 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mohs hardness | 2.25 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Brinell hardness | 70–95 MPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Number | 7440-69-9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discovery | Arabic alchemists (before AD 1000) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Isotopes of bismuth | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Bismuth is a chemical element with the symbol Bi and atomic number 83. It is a post-transition metal and one of the pnictogens, with chemical properties resembling its lighter group 15 siblings arsenic and antimony. Elemental bismuth occurs naturally, and its sulfide and oxide forms are important commercial ores. The free element is 86% as dense as lead. It is a brittle metal with a silvery-white color when freshly produced. Surface oxidation generally gives samples of the metal a somewhat rosy cast. Further oxidation under heat can give bismuth a vividly iridescent appearance due to thin-film interference. Bismuth is both the most diamagnetic element and one of the least thermally conductive metals known.
Bismuth used to be considered the element with the highest atomic mass whose nuclei do not spontaneously decay. However, in 2003 it was discovered to be extremely weakly radioactive. The metal's only primordial isotope, bismuth-209, undergoes alpha decay with a half-life about a billion times the estimated age of the universe.[8][9]
Bismuth metal has been known since ancient times. Before modern analytical methods bismuth's metallurgical similarities to lead and tin often led it to be confused with those metals. The etymology of "bismuth" is uncertain. The name may come from mid-sixteenth century Neo-Latin translations of the German words weiße Masse or Wismuth, meaning 'white mass', which were rendered as bisemutum or bisemutium.
Bismuth compounds account for about half the global production of bismuth. They are used in cosmetics; pigments; and a few pharmaceuticals, notably bismuth subsalicylate, used to treat diarrhea.[9] Bismuth's unusual propensity to expand as it solidifies is responsible for some of its uses, as in the casting of printing type.[9] Bismuth, when in its elemental form, has unusually low toxicity for a heavy metal.[9] As the toxicity of lead and the cost of its environmental remediation became more apparent during the 20th century, suitable bismuth alloys have gained popularity as replacements for lead. Presently, around a third of global bismuth production is dedicated to needs formerly met by lead.
- ^ "Standard Atomic Weights: Bismuth". CIAAW. 2005.
- ^ Prohaska, Thomas; Irrgeher, Johanna; Benefield, Jacqueline; Böhlke, John K.; Chesson, Lesley A.; Coplen, Tyler B.; Ding, Tiping; Dunn, Philip J. H.; Gröning, Manfred; Holden, Norman E.; Meijer, Harro A. J. (4 May 2022). "Standard atomic weights of the elements 2021 (IUPAC Technical Report)". Pure and Applied Chemistry. doi:10.1515/pac-2019-0603. ISSN 1365-3075.
- ^ a b Arblaster, John W. (2018). Selected Values of the Crystallographic Properties of Elements. Materials Park, Ohio: ASM International. ISBN 978-1-62708-155-9.
- ^ a b Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. p. 28. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- ^ Bi(0) state exists in a N-heterocyclic carbene complex of dibismuthene; see Deka, Rajesh; Orthaber, Andreas (9 May 2022). "Carbene chemistry of arsenic, antimony, and bismuth: origin, evolution and future prospects". Royal Society of Chemistry. 51 (22): 8540–8556. doi:10.1039/d2dt00755j. PMID 35578901. S2CID 248675805.
- ^ Weast, Robert (1984). CRC, Handbook of Chemistry and Physics. Boca Raton, Florida: Chemical Rubber Company Publishing. pp. E110. ISBN 0-8493-0464-4.
- ^ Kondev, F. G.; Wang, M.; Huang, W. J.; Naimi, S.; Audi, G. (2021). "The NUBASE2020 evaluation of nuclear properties" (PDF). Chinese Physics C. 45 (3): 030001. doi:10.1088/1674-1137/abddae.
- ^ Dumé, Belle (23 April 2003). "Bismuth breaks half-life record for alpha decay". Physicsworld.
- ^ a b c d Kean, Sam (2011). The Disappearing Spoon (and other true tales of madness, love, and the history of the world from the Periodic Table of Elements). New York/Boston: Back Bay Books. pp. 158–160. ISBN 978-0-316-051637.
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).