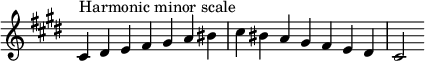Back دو مرتفع صغير Arabic Do sostingut menor Catalan دۆی بەرزی بچووک CKB Cis-Moll German Ντο δίεση ελάσσονα Greek C♯-minoro Esperanto Do sostenido menor Spanish Cis-moll Estonian دو دیز مینور Persian Cis-molliasteikko Finnish
| Relative key | E major |
|---|---|
| Parallel key | C-sharp major |
| Dominant key | G-sharp minor |
| Subdominant | F-sharp minor |
| Component pitches | |
| C♯, D♯, E, F♯, G♯, A, B | |
C-sharp minor is a minor scale based on C♯, with the pitches C♯, D♯, E, F♯, G♯, A, and B. Its key signature consists of four sharps.
The C-sharp natural minor scale is:
Changes needed for the melodic and harmonic versions of the scale are written in with accidentals as necessary. The C-sharp harmonic minor and melodic minor scales are:
Its relative major is E major. Its parallel major, C-sharp major, is usually written instead as the enharmonic key of D-flat major, since C-sharp major’s key signature with seven sharps is not normally used. Its enharmonic equivalent, D-flat minor, having eight flats including the B![]() , has a similar problem. Therefore, C-sharp minor is often used as the parallel minor for D-flat major. (The same enharmonic situation occurs with the keys of A-flat major and G-sharp minor, and in some cases, with the keys of G-flat major and F-sharp minor.)
, has a similar problem. Therefore, C-sharp minor is often used as the parallel minor for D-flat major. (The same enharmonic situation occurs with the keys of A-flat major and G-sharp minor, and in some cases, with the keys of G-flat major and F-sharp minor.)