
Back CE-20 French क्रायोजेनिक इंजन-20 Hindi CE-20 Croatian CE-20 ID CE-20 Japanese சி.இ-20 Tamil CE-20 Chinese
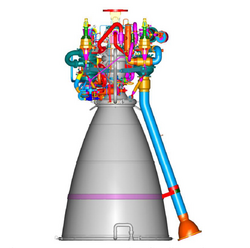 A computer model of CE-20 | |
| Country of origin | India |
|---|---|
| First flight | June 5, 2017 |
| Designer | LPSC, ISRO |
| Manufacturer | Hindustan Aeronautics Limited[1] |
| Application | Upper stage booster |
| Status | Active |
| Liquid-fuel engine | |
| Propellant | LOX / LH2 |
| Mixture ratio | 5.05 |
| Cycle | Gas Generator |
| Configuration | |
| Chamber | 1 |
| Nozzle ratio | 100 |
| Performance | |
| Thrust, vacuum | 186.36 kN (41,900 lbf) |
| Throttle range | 180–220 kN (40,000–49,000 lbf) |
| Chamber pressure | 6 MPa (870 psi) |
| Specific impulse, vacuum | 442 seconds (4.33 km/s) |
| Burn time | 640-800 seconds |
| Dimensions | |
| Dry mass | 588 kg (1,296 lb) |
| Used in | |
| Upper stage of LVM3 & NGLV | |
| References | |
| References | [2][3][4] |
The CE-20 is a cryogenic rocket engine developed by the Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre (LPSC), a subsidiary of the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO). It has been developed to power the upper stage of the LVM3.[5] It is the first Indian cryogenic engine to feature a gas-generator cycle.[6] The high thrust cryogenic engine is the most powerful upper stage cryogenic engine in operational service.[7]
Among the thrust levels for which CE-20 is qualified are 19 tonnes for ongoing satellite missions, 20 tonnes for the Gaganyaan, and an upgraded 22 tonnes for future launches like the Bharatiya Antariksha Station's BAS-01 Base Module.[8][9]
- ^ "HAL to produce cryogenic engines for ISRO". The Hindu. 27 April 2013. Archived from the original on 5 December 2013. Retrieved 2 November 2015.
- ^ "ISRO successfully tests Cryogenic Engine (CE-20) for GSLV Mk-III / Chandrayaan-2 Mission". ISRO. Archived from the original on 4 August 2022.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
AeroIndia2009_LPSC_1was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
AeroIndia2009_LPSC_2was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "Indigenous Cryogenic Engine Tested Successfully". www.isro.gov.in. Archived from the original on 2018-01-17. Retrieved 2018-01-17.
- ^ K. S. Jayaram (22 February 2016). "India's heavy-lift rocket on track for December debut following engine test". Spacenews.
- ^ Praveen, RS; Jayan, N; Bijukumar, KS; Jayaprakash, J; Narayanan, V; Ayyappan, G (February 2017). "Development of Cryogenic Engine for GSLV MkIII: Technological Challenges". IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering. 171 (1): 012059. Bibcode:2017MS&E..171a2059P. doi:10.1088/1757-899X/171/1/012059.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
:3was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Bagla, Pallava; Chowdhury, Shatabdi (29 June 2024). "Robotic Version Of Indian Space Station By 2028: ISRO Chief To NDTV". NDTV.com. Retrieved 2024-07-01.