
Back لاكتات الكالسيوم Arabic Kalsium laktat Azerbaijani کلسیوم لاوکتات AZB Lactat de calci Catalan Calciumlactat German Kalcia laktato Esperanto Lactato de calcio Spanish کلسیم لاکتات Persian Kalsiumlaktaatti Finnish Kalsium laktat ID
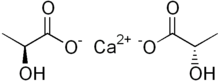 Calcium L-lactate
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Calcium bis(2-hydroxypropanoate) | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.011.278 |
| EC Number |
|
| E number | E327 (antioxidants, ...) |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H10CaO6 | |
| Molar mass | 218.22 g/mol |
| Appearance | white or off-white powder, slightly efflorescent |
| Density | 1.494 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 240 °C (464 °F; 513 K) (anhydrous) 120 °C (pentahydrate) |
| L-lactate, anhydrous, g/100 mL: 4.8 (10 °C), 5.8 (20 °C), 6.7 (25 °C), 8.5 (30 °C);[1][2] 7.9 g/100 mL (30 °C)[citation needed] | |
| Solubility | very soluble in methanol, insoluble in ethanol |
| Acidity (pKa) | 6.0-8.5 |
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.470 |
| Pharmacology | |
| A12AA05 (WHO) | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |

| |
| Warning | |
| H319 | |
| P264, P280, P305+P351+P338, P337+P313 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | Not applicable |
| No data | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Calcium lactate is a white crystalline salt with formula C
6H
10CaO
6, consisting of two lactate anions H
3C(CHOH)CO−
2 for each calcium cation Ca2+
. It forms several hydrates, the most common being the pentahydrate C
6H
10CaO
6·5H
2O.
Calcium lactate is used in medicine, mainly to treat calcium deficiencies; and as a food additive with E number of E327. Some cheese crystals consist of calcium lactate.[3][4]
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
vavwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
vav2was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Stephie Clark & Shantanu Agarwal (April 27, 2007). "Chapter 24: Cheddar and Related Hard Cheeses. 24.6: Crystal Formation". In Y. H. Hui (ed.). Handbook of Food Products Manufacturing (1st ed.). Wiley-Interscience. p. 589. ISBN 978-0470049648.
- ^ Phadungath, Chanokphat (2011). The Efficacy of Sodium Gluconate as a Calcium Lactate Crystal Inhibitor in Cheddar Cheese (Thesis). University of Minnesota. Archived from the original on May 5, 2021. Retrieved October 12, 2013.
