
Back Kategorie (wiskunde) Afrikaans فئة (رياضيات) Arabic Катэгорыя BE-X-OLD Категория (математика) Bulgarian Categoria (matemàtiques) Catalan Kategorie (matematika) Czech Kategori (matematik) Danish Kategorio (matematiko) Esperanto Categoría (matemáticas) Spanish Kategooria (matemaatika) Estonian
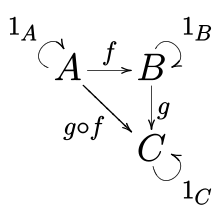
In mathematics, a category (sometimes called an abstract category to distinguish it from a concrete category) is a collection of "objects" that are linked by "arrows". A category has two basic properties: the ability to compose the arrows associatively and the existence of an identity arrow for each object. A simple example is the category of sets, whose objects are sets and whose arrows are functions.
Category theory is a branch of mathematics that seeks to generalize all of mathematics in terms of categories, independent of what their objects and arrows represent. Virtually every branch of modern mathematics can be described in terms of categories, and doing so often reveals deep insights and similarities between seemingly different areas of mathematics. As such, category theory provides an alternative foundation for mathematics to set theory and other proposed axiomatic foundations. In general, the objects and arrows may be abstract entities of any kind, and the notion of category provides a fundamental and abstract way to describe mathematical entities and their relationships.
In addition to formalizing mathematics, category theory is also used to formalize many other systems in computer science, such as the semantics of programming languages.
Two categories are the same if they have the same collection of objects, the same collection of arrows, and the same associative method of composing any pair of arrows. Two different categories may also be considered "equivalent" for purposes of category theory, even if they do not have precisely the same structure.
Well-known categories are denoted by a short capitalized word or abbreviation in bold or italics: examples include Set, the category of sets and set functions; Ring, the category of rings and ring homomorphisms; and Top, the category of topological spaces and continuous maps. All of the preceding categories have the identity map as identity arrows and composition as the associative operation on arrows.
The classic and still much used text on category theory is Categories for the Working Mathematician by Saunders Mac Lane. Other references are given in the References below. The basic definitions in this article are contained within the first few chapters of any of these books.
| Total | Associative | Identity | Divisible | Commutative | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Partial magma | Unneeded | Unneeded | Unneeded | Unneeded | Unneeded |
| Semigroupoid | Unneeded | Required | Unneeded | Unneeded | Unneeded |
| Small category | Unneeded | Required | Required | Unneeded | Unneeded |
| Groupoid | Unneeded | Required | Required | Required | Unneeded |
| Commutative groupoid | Unneeded | Required | Required | Required | Required |
| Magma | Required | Unneeded | Unneeded | Unneeded | Unneeded |
| Commutative magma | Required | Unneeded | Unneeded | Unneeded | Required |
| Quasigroup | Required | Unneeded | Unneeded | Required | Unneeded |
| Commutative quasigroup | Required | Unneeded | Unneeded | Required | Required |
| Unital magma | Required | Unneeded | Required | Unneeded | Unneeded |
| Commutative unital magma | Required | Unneeded | Required | Unneeded | Required |
| Loop | Required | Unneeded | Required | Required | Unneeded |
| Commutative loop | Required | Unneeded | Required | Required | Required |
| Semigroup | Required | Required | Unneeded | Unneeded | Unneeded |
| Commutative semigroup | Required | Required | Unneeded | Unneeded | Required |
| Associative quasigroup | Required | Required | Unneeded | Required | Unneeded |
| Commutative-and-associative quasigroup | Required | Required | Unneeded | Required | Required |
| Monoid | Required | Required | Required | Unneeded | Unneeded |
| Commutative monoid | Required | Required | Required | Unneeded | Required |
| Group | Required | Required | Required | Required | Unneeded |
| Abelian group | Required | Required | Required | Required | Required |
Any monoid can be understood as a special sort of category (with a single object whose self-morphisms are represented by the elements of the monoid), and so can any preorder.