
Back سفالوسپورین سی Persian Céphalosporine C French セファロスポリンC Japanese Cefalosporin C Serbo-Croatian Cefalosporin C Serbian
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
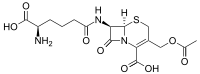
| IUPAC name
3-[(Acetyloxy)methyl]-7β-(N6-L-homoglutamino)-3,4-didehydrocepham-4-carboxylic acid
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(6R,7R)-3-[(Acetyloxy)methyl]-7-[(5R)-5-amino-5-carboxypentanamido]-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid | |
| Other names
7-(5-Amino-5-carboxyvaleramido)cephalosporanic acid
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.456 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C16H21N3O8S | |
| Molar mass | 415.42 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Cephalosporin C is an antibiotic of the cephalosporin class. It was isolated from a fungus of the genus Acremonium and first characterized in 1961.[1] Although not a very active antibiotic itself, synthetic analogs of cephalosporin C, such as cefalotin, became some of the first marketed cephalosporin antibiotic drugs.
Cephalosporin C strongly absorbs ultraviolet light, is stable to acid, is non-toxic and has in vivo activity in mice.[2] Cephalosporin C, which has a similar structure to penicillin N, was never commercialized.
Cephalosporin C was a lead compound for the discovery and production of many other cephalosporins.[2] Cephalosporins are drugs used for some people who are allergic to penicillin.
- ^ Abraham, E. P.; Newton, G. G. F. (1961). "Structure of cephalosporin C". Biochemical Journal. 79 (2): 377–393. doi:10.1042/bj0790377. PMC 1205850. PMID 13681080.
- ^ a b Kardos, Nelson; Demain, Arnold L. (November 2011). "Penicillin: the medicine with the greatest impact on therapeutic outcomes". Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology. 92 (4): 677–687. doi:10.1007/s00253-011-3587-6. ISSN 0175-7598. PMID 21964640. S2CID 39223087.