
Back بينيين بريدي Arabic Trescripción del sistema postal chinu AST Transcripció del sistema postal xinès Catalan Transkriptionssystem der chinesischen Post German Transcripción del sistema postal chino Spanish Pinyin postal French Peromawian pos Tiongkok ID Romanizzazione del sistema postale cinese Italian 郵政式 Japanese 우정식 병음 Korean
| Postal romanization 郵政式拼音;邮政式拼音 | |
|---|---|
| Script type | romanization |
Time period | 1892–2002 |
| Languages | Chinese |
| Chinese postal romanization | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
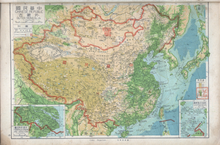 A map of China with romanizations published in 1947 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 郵政式拼音 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 邮政式拼音 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Literal meaning | Postal-style romanization system | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Postal romanization[1] was a system of transliterating place names in China developed by postal authorities in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. For many cities, the corresponding postal romanization was the most common English-language form of the city's name from the 1890s until the 1980s, when postal romanization was replaced by pinyin, but the system remained in place on Taiwan until 2002.
In 1892, Herbert Giles created a romanization system called the Nanking syllabary. The Imperial Maritime Customs Post Office would cancel postage with a stamp that gave the city of origin in Latin letters, often romanized using Giles's system. In 1896, the Customs Post was combined with other postal services and renamed the Chinese Imperial Post. As a national agency, the Imperial Post was an authority on Chinese place names.[2]
When the Wade–Giles system became widespread, some argued that the post office should adopt it. This idea was rejected at a conference held in 1906 in Shanghai. Instead, the conference formally adopted Nanking syllabary.[3] This decision allowed the post office to continue to use various romanizations that it had already selected. Wade–Giles romanization is based on the Beijing dialect, a pronunciation standard since the 1850s. The use of Nanking syllabary did not suggest that the post office considered Nanjing pronunciation to be standard. Rather, it was an attempt to accommodate a variety of Mandarin pronunciations with a single romanization system.
- ^ Postal Romanization. Taipei: Directorate General of Posts. 1961. OCLC 81619222.
- ^ Harris (2009), p. 96.
- ^ Harris (2009), p. 101.