
Back Tsjoekotkasee Afrikaans بحر تشوكشي Arabic Mar de Chukotka AST Çukot dənizi Azerbaijani چوکوچی دنیزی AZB Чукот диңгеҙе Bashkir Чукоцкае мора Byelorussian Чукотско море Bulgarian চুকচি সাগর Bengali/Bangla Čukotsko more BS
| Chukchi Sea | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Location | North Asia and Northern America |
| Coordinates | 69°N 172°W / 69°N 172°W |
| Type | Sea |
| Basin countries | Russia and United States |
| Surface area | 620,000 km2 (240,000 sq mi) |
| Average depth | 80 m (260 ft) |
| Water volume | 50,000 km3 (4.1×1010 acre⋅ft) |
| References | [1][2][3] |

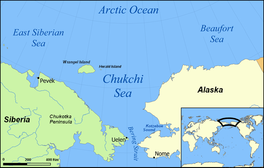
The Chukchi Sea (Russian: Чуко́тское мо́ре, romanized: Chukótskoye móre, IPA: [tɕʊˈkotskəjə ˈmorʲe]), sometimes referred to as the Chuuk Sea, Chukotsk Sea[4] or the Sea of Chukotsk,[5] is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It is bounded on the west by the Long Strait, off Wrangel Island, and in the east by Point Barrow, Alaska, beyond which lies the Beaufort Sea. The Bering Strait forms its southernmost limit and connects it to the Bering Sea and the Pacific Ocean. The principal port on the Chukchi Sea is Uelen in Russia. The International Date Line crosses the Chukchi Sea from northwest to southeast. It is displaced eastwards to avoid Wrangel Island as well as the Chukotka Autonomous Okrug on the Russian mainland.
- ^ R. Stein, Arctic Ocean Sediments: Processes, Proxies, and Paleoenvironment, p. 37
- ^ Beaufort Sea, Great Soviet Encyclopedia (in Russian)
- ^ Beaufort Sea, Encyclopædia Britannica on-line
- ^ "education.rec.org Seas and Oceans: The Chukotsk Sea". Archived from the original on 2021-10-17. Retrieved 2019-04-11.
- ^ Owen, Richard (15 October 1983). "Race against time to save ice-bound ships". The Times. No. 61664. London. col D, p. 6.