
Back مستعمرة موريتانيا Arabic Colonia de Mauritania Spanish Colonie de la Mauritanie French Frans-Mauritanië Dutch Mauritânia colonial Portuguese Колониальная Мавритания Russian Franska Mauretanien Swedish
Colony of Mauritania Colonie de la Mauritanie مستعمرة موريتانيا Mustaemara al-muritania | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1903–1960 | |||||||||||
| Anthem: La Marseillaise | |||||||||||
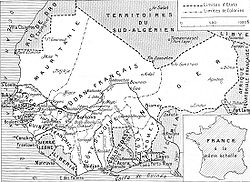 Map of the seven colonies of French West Africa in 1936. Note that the eighth colony, French Upper Volta, was in this period parceled between its neighbors. French Sudan also contains a large portion of what is today the eastern half of Mauritania. | |||||||||||
| Status | Constituent of French West Africa | ||||||||||
| Capital | Saint-Louis (exterritorial) (1903–1957) Nouakchott (1957–1960) | ||||||||||
| Common languages | French Arabic | ||||||||||
| Government | Protectorate (1903–1904) Civil territory (1904–1920) Colony (1920–1946) Overseas territory (1946–1958) Autonomous republic (1958–1960) | ||||||||||
| Commissioner | |||||||||||
• 1903–1905 | Xavier Coppolani | ||||||||||
• 1916–1920 | Nicolas Jules Henri Gaden | ||||||||||
| Lieutenant Governor | |||||||||||
• 1920–1926 | Nicolas Jules Henri Gaden | ||||||||||
• 1956–1958 | Albert Jean Mouragues | ||||||||||
| High Commissioner | |||||||||||
• 1958–1959 | Henri Joseph Marie Bernard | ||||||||||
• 1959–1960 | Amédée Joseph Émile Jean Pierre Anthonioz | ||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||
• Protectorate established | May 12, 1903 | ||||||||||
• Civil territory | October 18, 1904 | ||||||||||
• Colony established | January 12, 1920 | ||||||||||
• Status changed to overseas territory | October 27, 1946 | ||||||||||
• Autonomy | November 28, 1958 | ||||||||||
• Independence | November 28, 1960 | ||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||
| 1936[1] | 833,977 km2 (322,000 sq mi) | ||||||||||
| 1948[2] | 942,995 km2 (364,092 sq mi) | ||||||||||
| Population | |||||||||||
• 1936[1] | 383,000 | ||||||||||
• 1948[2] | 518,000 | ||||||||||
| Currency | French West African franc (1903–1945) CFA franc (1945–1960) | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| History of Mauritania |
|---|
 |
|
|
The period from the mid-nineteenth to mid-twentieth centuries is the colonial period in Mauritania.
