
Back تشريح مقارن Arabic Müqayisəli anatomiya Azerbaijani Uporedna anatomija BS Anatomia comparada Catalan Srovnávací anatomie Czech Anatomeg gymharol Welsh Vergleichende Anatomie German Kompara anatomio Esperanto Anatomía comparada Spanish Võrdlev anatoomia Estonian
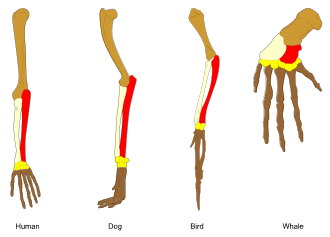
Comparative anatomy is the study of similarities and differences in the anatomy of different species. It is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny[1] (the evolution of species).
The science began in the classical era, continuing in the early modern period with work by Pierre Belon who noted the similarities of the skeletons of birds and humans.
Comparative anatomy has provided evidence of common descent, and has assisted in the classification of animals.[2]
- ^ Gaucher EA, Kratzer JT, Randall RN (January 2010). "Deep phylogeny--how a tree can help characterize early life on Earth". Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology. 2 (1): a002238. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a002238. PMC 2827910. PMID 20182607.
- ^ National Academy of Sciences (US) (22 April 1999). Science and Creationism. doi:10.17226/6024. ISBN 978-0-309-06406-4. PMID 25101403.