
Back Coprates (Gradfeld) German Coprates (cuadrángulo) Spanish Quadrangle de Coprates French कोप्रेट्स चतुष्कोण Hindi Maglia Coprates Italian Quadrângulo de Coprates Portuguese Coprates dörtgeni Turkish Квадрангл Coprates Ukrainian Cuadràngoło de Coprates VEC 科普莱特斯区 Chinese
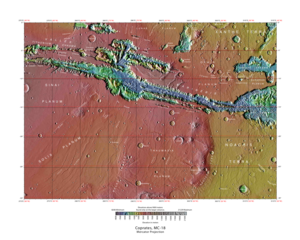 Map of Coprates quadrangle from Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter (MOLA) data. The highest elevations are red and the lowest are blue. | |
| Coordinates | 15°00′S 67°30′W / 15°S 67.5°W |
|---|---|

The Coprates quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Coprates quadrangle is also referred to as MC-18 (Mars Chart-18).[1] The Coprates quadrangle contains parts of many of the old classical regions of Mars: Sinai Planum, Solis Planum, Thaumasia Planum, Lunae Planum, Noachis Terra, and Xanthe Terra.
The name Coprates refers to Coprates Chasma, a central trough of the Valles Marineris, named after the Greek name of the Dez River in Persia.[2]
The Coprates quadrangle goes from 45° to 90° west longitude and 0° to 30° south latitude on Mars. Coprates quadrangle is famous for depicting the "Grand Canyon of Mars", the Valles Marineris Canyon System. Signs of water exist in this quadrangle, with ancient river valleys and networks of stream channels showing up as inverted terrain and lakes inside of Valles Marineris.[3]
- ^ Davies, M.E.; Batson, R.M.; Wu, S.S.C. "Geodesy and Cartography" in Kieffer, H.H.; Jakosky, B.M.; Snyder, C.W.; Matthews, M.S., Eds. Mars. University of Arizona Press: Tucson, 1992.
- ^ Blunck, J. 1982. Mars and its Satellites. Exposition Press. Smithtown, N.Y.
- ^ Cabrol, N. and E. Grin (eds.). 2010. Lakes on Mars. Elsevier. NY