
Back دلفینین AZB Delphinin German Delfinina Spanish دلفینین Persian Delphinine French Delphinin NB Дельфинин Russian Delfinin Serbo-Croatian Delfinin Serbian Delfinin Swedish
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
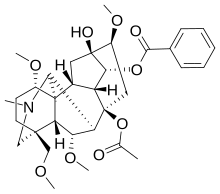
8-(Acetyloxy)-13-hydroxy-1,6,16-trimethoxy-4-(methoxymethyl)-20-methylaconitan-14-yl benzoate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.377 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C33H45NO9 | |
| Molar mass | 599.712 |
| Appearance | colorless solid |
| Melting point | 197 to 199 °C (387 to 390 °F; 470 to 472 K) |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
Toxic |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Delphinine is a toxic diterpenoid alkaloid found in plants from the Delphinium (larkspur) and Atragene (a clematis) genera, both in the family Ranunculaceae.[1] Delphinine is the principal alkaloid found in Delphinium staphisagria seeds – at one time, under the name stavesacre, a very well known herbal treatment for body lice.[2] It is related in structure and has similar effects to aconitine, acting as an allosteric modulator of voltage gated sodium channels,[3] and producing low blood pressure, slowed heart rate and abnormal heart rhythms. These effects make it highly poisonous (LD50 1.5–3.0 mg/kg in rabbit and dog; frogs are ~10x more susceptible).[4] While it has been used in some alternative medicines (e.g. in herbal medicine[5][6]), most of the medical community does not recommend using it due to its extreme toxicity.
- ^ Harbourne JB, Baxter H, eds. (1993). Phytochemical Dictionary. London: Taylor & Francis. p. 148.
- ^ "A Modern Herbal | Stavesacre".
- ^ Turabekova MA, Rasulev BF, Levkovich MG, Abdullaev ND, Leszczynski J (April 2008). "Aconitum and Delphinium sp. alkaloids as antagonist modulators of voltage-gated Na+ channels. AM1/DFT electronic structure investigations and QSAR studies". Computational Biology and Chemistry. 32 (2): 88–101. doi:10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2007.10.003. PMC 5001567. PMID 18201930.
- ^ Benn MH, Jacyno JM (1983). Pelletier SW (ed.). "Chapter 4". The Alkaloids: Chemical and Biological Perspectives. 1. New York: Wiley: 153–210.
- ^ Desai HK, Hart BP, Caldwell RW, Jianzhong-Huang JH, Pelletier SW (June 1998). "Certain norditerpenoid alkaloids and their cardiovascular action". Journal of Natural Products. 61 (6): 743–8. doi:10.1021/np970499j. PMID 9644057.
- ^ Díaz JG, Ruiz JG, de La Fuente G (August 2000). "Alkaloids from Delphinium staphisagria". Journal of Natural Products. 63 (8): 1136–9. doi:10.1021/np990453l. PMID 10978212.