
Back Digitale televisie Afrikaans تلفزة رقمية Arabic Televisión dixital AST Лічбавае тэлебачаньне BE-X-OLD Цифрова телевизия Bulgarian डिजिटल टीवी Bihari Televisió digital Catalan Digitální televize Czech Digitalt tv Danish Digitales Fernsehen German
This article needs additional citations for verification. (May 2010) |
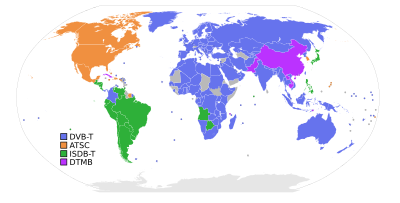
| List of digital television broadcast standards |
|---|
| DVB standards (countries) |
| ATSC standards (countries) |
|
| ISDB standards (countries) |
| DTMB standards (countries) |
| DMB standard (countries) |
| Codecs |
|
| Terrestrial Frequency bands |
| Satellite Frequency bands |
Digital television (DTV) is the transmission of television signals using digital encoding, in contrast to the earlier analog television technology which used analog signals. At the time of its development it was considered an innovative advancement and represented the first significant evolution in television technology since color television in the 1950s.[1] Modern digital television is transmitted in high-definition television (HDTV) with greater resolution than analog TV. It typically uses a widescreen aspect ratio (commonly 16:9) in contrast to the narrower format (4:3) of analog TV. It makes more economical use of scarce radio spectrum space; it can transmit up to seven channels in the same bandwidth as a single analog channel,[2] and provides many new features that analog television cannot. A transition from analog to digital broadcasting began around 2000. Different digital television broadcasting standards have been adopted in different parts of the world; below are the more widely used standards:
- Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB) uses coded orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) modulation and supports hierarchical transmission. This standard has been adopted in Europe, Africa, Asia and Australia, for a total of approximately 60 countries.
- Advanced Television System Committee (ATSC) standard uses eight-level vestigial sideband (8VSB) for terrestrial broadcasting. This standard has been adopted by 9 countries: the United States, Canada, Mexico, South Korea, Bahamas, Jamaica, the Dominican Republic, Haiti and Suriname.[citation needed]
- Integrated Services Digital Broadcasting (ISDB) is a system designed to provide good reception to fixed receivers and also portable or mobile receivers. It utilizes OFDM and two-dimensional interleaving. It supports hierarchical transmission of up to three layers and uses MPEG-2 video and Advanced Audio Coding. This standard has been adopted in Japan and the Philippines. ISDB-T International is an adaptation of this standard using H.264/MPEG-4 AVC, which has been adopted in most of South America as well as Botswana and Angola.
- Digital Terrestrial Multimedia Broadcast (DTMB) adopts time-domain synchronous (TDS) OFDM technology with a pseudo-random signal frame to serve as the guard interval (GI) of the OFDM block and the training symbol. The DTMB standard has been adopted in China, including Hong Kong and Macau.[3]
- Digital Multimedia Broadcasting (DMB) is a digital radio transmission technology developed in South Korea[4][5][6] as part of the national information technology project for sending multimedia such as TV, radio and datacasting to mobile devices such as mobile phones, laptops and GPS navigation systems.
- ^ Kruger, Lennard G. (2002). Digital Television: An Overview. New York: Nova Publishers. ISBN 1-59033-502-3.
- ^ "HDTV Set Top Boxes and Digital TV Broadcast Information". Archived from the original on 22 May 2016. Retrieved 28 June 2014.
- ^ Ong, C. Y., Song, J., Pan, C., & Li, Y.(2010, May). Technology and Standards of Digital Television Terrestrial Multimedia Broadcasting [Topics in Wireless Communications], IEEE Communications Magazine, 48(5),119–127
- ^ "Korea's Terrestrial DMB: Germany to begin broadcast this May". ZDNet Korea. 2006-04-06. Retrieved 2010-06-17.
- ^ "picturephoning.com: DMB". Textually.org. Archived from the original on 2010-08-09. Retrieved 2010-06-17.
- ^ "South Korea : Social Media 답변 내용 : 악어새 – 리포트월드". Reportworld.co.kr. Archived from the original on 2009-08-17. Retrieved 2010-06-17.