
Back تفكك الإمبراطورية النمساوية المجرية Arabic Распад Аўстра-Венгерскай імперыі Byelorussian Распад Аўстра-Вугоршчыны BE-X-OLD Австрин-Мажарчоьнан импери йохар CE Zánik Rakousko-Uherska Czech Disgregación de Austria-Hungría Spanish فروپاشی اتریش-مجارستان Persian Itävalta-Unkarin hajoaminen Finnish פירוק האימפריה האוסטרו-הונגרית HE Raspad Austro-Ugarske Croatian
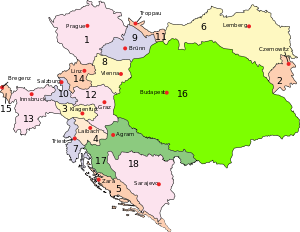 Kingdoms and countries of Austria–Hungary: Cisleithania (Empire of Austria[1]): 1. Bohemia, 2. Bukovina, 3. Carinthia, 4. Carniola, 5. Dalmatia, 6. Galicia, 7. Küstenland, 8. Lower Austria, 9. Moravia, 10. Salzburg, 11. Silesia, 12. Styria, 13. Tyrol, 14. Upper Austria, 15. Vorarlberg; Transleithania (Kingdom of Hungary[1]): 16. Hungary proper 17. Croatia-Slavonia; Joint control by Austria and Hungary: 18. Bosnia and Herzegovina (Austro-Hungarian condominium) |
The dissolution of Austria-Hungary was a major political event that occurred as a result of the growth of internal social contradictions and the separation of different parts of Austria-Hungary. The more immediate reasons for the collapse of the state were World War I, the 1918 crop failure, general starvation and the economic crisis.[citation needed] The Austro-Hungarian Empire had additionally been weakened over time by a widening gap between Hungarian and Austrian interests.[2] Furthermore, a history of chronic overcommitment rooted in the 1815 Congress of Vienna in which Metternich pledged Austria to fulfill a role that necessitated unwavering Austrian strength and resulted in overextension.[2] Upon this weakened foundation, additional stressors during World War I catalyzed the collapse of the empire. The 1917 October Revolution and the Wilsonian peace pronouncements from January 1918 onward encouraged socialism on the one hand, and nationalism on the other, or alternatively a combination of both tendencies, among all peoples of the Habsburg monarchy.[3]
The remaining territories inhabited by divided peoples fell into the composition of existing or newly formed states. Legally, the collapse of the empire was formalized in the September 1919 Treaty of Saint-Germain-en-Laye with Austria, which also acted as a peace treaty after the First World War, and in the June 1920 Treaty of Trianon with Hungary. Later, additional territories were ceded to other countries.
- ^ a b Headlam, James Wycliffe (1911). . In Chisholm, Hugh (ed.). Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 3 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 2–39.
- ^ a b Evans, R. J. W. (2020-04-02). "Remembering the Fall of the Habsburg Monarchy One Hundred Years on: Three Master Interpretations". Austrian History Yearbook. 51: 269–291. doi:10.1017/s0067237820000181. ISSN 0067-2378.
- ^ "The collapse of Austria-Hungary". Encyclopædia Britannica.