
Back Idioma armeniu oriental AST Şərqi erməni dili Azerbaijani Armeni oriental Catalan Ostarmenisch German Orient-armena lingvo Esperanto Idioma armenio oriental Spanish Idaarmeenia keel Estonian زبان ارمنی شرقی Persian Arménien oriental French Armeniañe'ẽ kuarahyresẽgua Guarani
This article needs additional citations for verification. (April 2023) |
| Eastern Armenian | |
|---|---|
| Արեւելահայերեն | |
| Native to | Armenia, Iran, Georgia, Russia, Ukraine, Central Asia |
Native speakers | 3.8 million (2013)[1] |
Indo-European
| |
| Armenian alphabet (virtually always in the reformed orthography, except in Iran) | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | hy |
| ISO 639-2 | arm (B) hye (T) |
| ISO 639-3 | hye |
| Glottolog | nucl1235 |
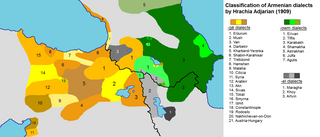 Map of the Armenian dialects in early 20th century: -owm dialects, corresponding to Eastern Armenian, are shown in green. | |
 |
| History of the Armenian language |
|---|
|
|
Armenian alphabet Romanization of Armenian |
Eastern Armenian (Armenian: Արեւելահայերեն, romanized: Arevelahayeren) is one of the two standardized forms of Modern Armenian, the other being Western Armenian. The two standards form a pluricentric language.
Eastern Armenian is spoken in Armenia, Russia, as well as Georgia, and by the Armenian community in Iran. Although the Eastern Armenian spoken by Armenians in Armenia and Iranian-Armenians are similar, there are pronunciation differences with different inflections.[2] Armenians from Iran also have some words that are unique to them. Due to migrations of speakers from Armenia and Iran to the Armenian diaspora, the dialect is now very prominent in countries and regions where only Western Armenian was used. Eastern Armenian is based on the Yerevan dialect.
- ^ Eastern Armenian at Ethnologue (25th ed., 2022)

- ^ Dolatian H, Sharifzadeh A, Vaux B (2023). A grammar of Iranian Armenian: Parskahayeren or Iranahayeren (pdf). Berlin: Language Science Press. doi:10.5281/zenodo.8177018. ISBN 9783961104192.