
Back Elektriese lading Afrikaans ቻርጅ Amharic شحنة كهربائية Arabic تعميرة د التريسينتي ARY Carga llétrica AST Elektrik yükü Azerbaijani الکتریک یوکو AZB Elektrische Lodung BAR Электрычны зарад Byelorussian Электрычны зарад BE-X-OLD
| Electric charge | |
|---|---|
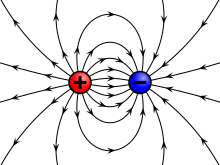 Electric field of a positive and a negative point charge | |
Common symbols | q |
| SI unit | coulomb (C) |
Other units | |
| In SI base units | A⋅s |
| Extensive? | yes |
| Conserved? | yes |
| Dimension | |
| Articles about |
| Electromagnetism |
|---|
 |
Electric charge (symbol q, sometimes Q) is a physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field. Electric charge can be positive or negative. Like charges repel each other and unlike charges attract each other. An object with no net charge is referred to as electrically neutral. Early knowledge of how charged substances interact is now called classical electrodynamics, and is still accurate for problems that do not require consideration of quantum effects.
Electric charge is a conserved property: the net charge of an isolated system, the quantity of positive charge minus the amount of negative charge, cannot change. Electric charge is carried by subatomic particles. In ordinary matter, negative charge is carried by electrons, and positive charge is carried by the protons in the nuclei of atoms. If there are more electrons than protons in a piece of matter, it will have a negative charge, if there are fewer it will have a positive charge, and if there are equal numbers it will be neutral. Charge is quantized: it comes in integer multiples of individual small units called the elementary charge, e, about 1.602×10−19 C,[1] which is the smallest charge that can exist freely. Particles called quarks have smaller charges, multiples of 1/3e, but they are found only combined in particles that have a charge that is an integer multiple of e. In the Standard Model, charge is an absolutely conserved quantum number. The proton has a charge of +e, and the electron has a charge of −e.
Today, a negative charge is defined as the charge carried by an electron and a positive charge is that carried by a proton. Before these particles were discovered, a positive charge was defined by Benjamin Franklin as the charge acquired by a glass rod when it is rubbed with a silk cloth.
Electric charges produce electric fields.[2] A moving charge also produces a magnetic field.[3] The interaction of electric charges with an electromagnetic field (a combination of an electric and a magnetic field) is the source of the electromagnetic (or Lorentz) force,[4] which is one of the four fundamental interactions in physics. The study of photon-mediated interactions among charged particles is called quantum electrodynamics.[5]
The SI derived unit of electric charge is the coulomb (C) named after French physicist Charles-Augustin de Coulomb. In electrical engineering it is also common to use the ampere-hour (A⋅h). In physics and chemistry it is common to use the elementary charge (e) as a unit. Chemistry also uses the Faraday constant, which is the charge of one mole of elementary charges.
- ^ "2022 CODATA Value: elementary charge". The NIST Reference on Constants, Units, and Uncertainty. NIST. May 2024. Retrieved 2024-05-18.
- ^ Chabay, Ruth; Sherwood, Bruce (2015). Matter and interactions (4th ed.). Wiley. p. 867.
- ^ Chabay, Ruth; Sherwood, Bruce (2015). Matter and interactions (4th ed.). Wiley. p. 673.
- ^ Chabay, Ruth; Sherwood, Bruce (2015). Matter and interactions (4th ed.). Wiley. p. 942.
- ^ Rennie, Richard; Law, Jonathan, eds. (2019). "Quantum electrodynamics". A Dictionary of Physics (8th ed.). Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780198821472.
