
Back مجلس الشراكة الأوروبية الأطلسية Arabic Avro-Atlantik Tərəfdaşlıq Şurası Azerbaijani Савет еўраатлантычнага партнёрства Byelorussian Euroatlantická rada partnerství Czech Euro-Atlantiske Partnerskabsråd Danish Euro-Atlantischer Partnerschaftsrat German Conseil de partenariat euro-atlantique French Euro-atlanti Partnerségi Tanács Hungarian Partenariato Euro-Atlantico Italian 欧州・大西洋パートナーシップ理事会 Japanese
 EAPC logo | |
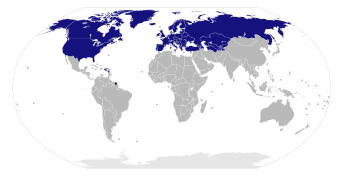 Member Suspended member | |
| Abbreviation | EAPC |
|---|---|
| Formation | 29 May 1997 |
| Headquarters | NATO Headquarters, Brussels, Belgium |
| Membership | 50 countries (including Russia and Belarus who are currently suspended) |
| Website | Euro-Atlantic Partnership Council |
This article needs to be updated. The reason given is: Needs more information regarding suspension of Russia and Belarus following Russian invasion of Ukraine. (August 2024) |
The Euro-Atlantic Partnership Council (EAPC) is a post–Cold War, North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) institution. The EAPC is a multilateral forum created to improve relations between NATO and non-NATO countries in Europe and Central Asia. States meet to cooperate and discuss political and security issues. It was formed on 29 May 1997 at a Ministers’ meeting held in Sintra, Portugal, as the successor to the North Atlantic Cooperation Council (NACC), which was created in 1991.[1]
The EAPC provides an overall political framework for NATO’s cooperation with its partner countries in the Euro-Atlantic area. It works alongside the Partnership for Peace (PfP), which was created in January 1994. There are 50 members, including all 32 NATO member countries and 18 Partnership for Peace countries.[2] Of its members, the United States has had a notable role in the council. In the post-Cold War era, the United States served as one of the key members of the EAPC that continued to push for engagement with Russia, which is an EAPC partner country.
Following the Russian invasion of Ukraine, Russia and Belarus were suspended from the Council.[3]
- ^ NATO (June 22, 2021). "Euro-Atlantic Partnership".
- ^ "Euro-Atlantic Partnership Council (EAPC)". The Nuclear Threat Initiative. Retrieved 2022-03-18.
- ^ NATO. "NATO's partnerships". NATO. Retrieved 2024-08-24.