
Back انتشار مسهل Arabic Difusió facilitada Catalan Erleichterte Diffusion German Difusión facilitada Spanish انتشار تسهیلشده Persian Fasilitoitunut diffuusio Finnish Diffusion facilitée French Potpomognuta difuzija Croatian 촉진 확산 Korean Gefaciliteerde diffusie Dutch
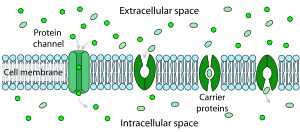
Facilitated diffusion (also known as facilitated transport or passive-mediated transport) is the process of spontaneous passive transport (as opposed to active transport) of molecules or ions across a biological membrane via specific transmembrane integral proteins.[1] Being passive, facilitated transport does not directly require chemical energy from ATP hydrolysis in the transport step itself; rather, molecules and ions move down their concentration gradient according to the principles of diffusion.

Facilitated diffusion differs from simple diffusion in several ways:
- The transport relies on molecular binding between the cargo and the membrane-embedded channel or carrier protein.
- The rate of facilitated diffusion is saturable with respect to the concentration difference between the two phases; unlike free diffusion which is linear in the concentration difference.
- The temperature dependence of facilitated transport is substantially different due to the presence of an activated binding event, as compared to free diffusion where the dependence on temperature is mild.[2]

Polar molecules and large ions dissolved in water cannot diffuse freely across the plasma membrane due to the hydrophobic nature of the fatty acid tails of the phospholipids that comprise the lipid bilayer. Only small, non-polar molecules, such as oxygen and carbon dioxide, can diffuse easily across the membrane. Hence, small polar molecules are transported by proteins in the form of transmembrane channels. These channels are gated, meaning that they open and close, and thus deregulate the flow of ions or small polar molecules across membranes, sometimes against the osmotic gradient. Larger molecules are transported by transmembrane carrier proteins, such as permeases, that change their conformation as the molecules are carried across (e.g. glucose or amino acids). Non-polar molecules, such as retinol or lipids, are poorly soluble in water. They are transported through aqueous compartments of cells or through extracellular space by water-soluble carriers (e.g. retinol binding protein). The metabolites are not altered because no energy is required for facilitated diffusion. Only permease changes its shape in order to transport metabolites. The form of transport through a cell membrane in which a metabolite is modified is called group translocation transportation.
Glucose, sodium ions, and chloride ions are just a few examples of molecules and ions that must efficiently cross the plasma membrane but to which the lipid bilayer of the membrane is virtually impermeable. Their transport must therefore be "facilitated" by proteins that span the membrane and provide an alternative route or bypass mechanism. Some examples of proteins that mediate this process are glucose transporters, organic cation transport proteins, urea transporter, monocarboxylate transporter 8 and monocarboxylate transporter 10.
- ^ Pratt CA, Voet D, Voet JG (2002). Fundamentals of biochemistry upgrade. New York: Wiley. pp. 264–266. ISBN 0-471-41759-9.
- ^ Friedman, Morton (2008). Principles and models of biological transport. Springer. ISBN 978-0387-79239-2.