
Back Erster Tag der Somme-Schlacht German Sommen taistelun ensimmäinen päivä Finnish 索姆河戰役首日 Chinese
| First day on the Somme | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Battle of the Somme (First World War) | |||||||
 Battle of the Somme, 1 July – 18 November 1916 | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
Douglas Haig Henry Rawlinson Ferdinand Foch Émile Fayolle | Fritz von Below | ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
|
13 British divisions 6 French divisions | 6 divisions | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
|
British: 57,470 (19,240 killed) French: 1,590 | 6,226–12,000 | ||||||
| In the German ten-day casualty accounting period (10 tägigen Truppenkrankenrapporten) for 1 to 10 July, there were 46,319 casualties and 7,539 men reported sick.[1] | |||||||
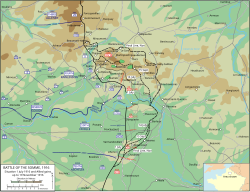
The first day on the Somme (1 July 1916) was the beginning of the Battle of Albert (1–13 July) the name given by the British to the first two weeks of the Battle of the Somme (1 July–18 November) in the First World War. Nine corps of the French Sixth Army and the British Fourth and Third armies attacked the German 2nd Army (General Fritz von Below). The attack was from Foucaucourt south of the Somme, northwards across the Somme and the Ancre to Serre and Gommecourt, 2 mi (3.2 km) beyond, in the Third Army area. The objective of the attack was to capture the German first and second defensive positions from Serre south to the Albert–Bapaume road and the first position from the road south to Foucaucourt.
The German defence south of the road mostly collapsed and the French had complete success on both banks of the Somme, as did the British from Maricourt on the army boundary with the French northwards. XIII Corps took Montauban and reached all its objectives, XV Corps captured Mametz and isolated Fricourt. The III Corps attack on both sides of the Albert–Bapaume road was a disaster, making only a short advance south of La Boisselle, where the 34th Division suffered the most casualties of any Allied division on 1 July. Further north, X Corps captured part of the Leipzig Redoubt (an earthwork fortification), failed opposite Thiepval and had a great but temporary success on the left flank, where the German front line was overrun and Schwaben and Stuff redoubts captured by the 36th (Ulster) Division.
German counter-attacks during the afternoon recaptured most of the lost ground north of the Albert–Bapaume road and more British attacks against Thiepval were costly failures. On the north bank of the Ancre, the attack of VIII Corps was a costly failure, with large numbers of British troops being shot down in no man's land. The VII Corps diversion at Gommecourt was also costly, with only a partial and temporary advance south of the village. The German defeats, from Foucaucourt to the Albert–Bapaume road, left the German defence on the south bank incapable of resisting another attack; a substantial German retreat began from the Flaucourt plateau to the west bank of the Somme close to Péronne. North of the Somme in the British area, Fricourt was abandoned by the Germans overnight.
Several truces were observed to recover wounded from no man's land on the British front; the Third Army diversion at Gommecourt cost 6,758 casualties against 1,212 German and the combined casualty count with the Fourth Army reached 57,470, (19,240 of which had been fatal). The French Sixth Army suffered 1,590 casualties and the German 2nd Army suffered 10,000–12,000 casualties. Orders were issued to the Anglo-French armies to continue the offensive on 2 July; a German counter-attack on the north bank of the Somme by the 12th Division, intended for the night of 1/2 July, took until dawn on 2 July to begin and was destroyed by the French and British troops opposite. Since 1 July 1916, the British casualties on the First Day and the "meagre gains" have been a source of grief and controversy in Britain.
- ^ Whitehead 2013, pp. 474–477.
