Following its withdrawal from the European Union on 31 January 2020, the United Kingdom began negotiations on several free trade agreements to remove or reduce tariff and non-tariff barriers to trade, both to establish new agreements and to replace previous EU trade agreements. Withdrawal ended 47 years of membership during which all its trading agreements were negotiated by the European Commission on behalf of the bloc. The UK did not actually withdraw from the European Single Market and the European Union Customs Union (and its trade agreements) until 31 December 2020.
These treaties are divided into two types of free trade agreements: continuity agreements and 'new' agreements. Continuity agreements, also named rollover agreements, make use of a mutatis mutandis concept in order to quickly replicate the existing EU agreements, only having to call out those minor areas of differentiation. Most continuity treaties were provisionally applied, or through a "bridging mechanism", thus continuity was achieved.[1] Trade agreements negotiated after Brexit are termed 'new', or enhanced agreements: these agreements have been negotiated from scratch or have been renegotiated to expand the deal since Brexit.[2]
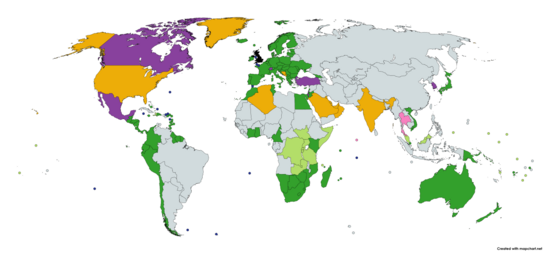
As of December 2024[update], the United Kingdom has 39 active free trade agreements with nations and trade blocs, covering 102 countries and territories.[3][1] Five of these are 'new' trade agreements, such as with Australia and New Zealand.[4] The UK is also a member of the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership. The remaining 33 are continuity agreements. Furthermore, the UK has a customs union with its three Crown Dependencies.[5] The UK has further arrangements covering free trade with its 14 British Overseas Territories.[6]
The United Kingdom has only suspended negotiations for a trade deal on one occasion; it suspended negotiations for a post-Brexit Canada Free Trade Agreement on 25 January 2024.[7]
- ^ a b Department for International Trade (3 November 2022). "UK trade agreements in effect". GOV.UK. Archived from the original on 24 December 2024. Retrieved 24 December 2024.
- ^ Eiser, David; McEwen, Nicola; Roy, Graeme (7 April 2021). "The Trade Policies of Brexit Britain: the Influence of and Impacts on the Devolved Nations" (PDF). Brill Publishers. Archived from the original (PDF) on 18 July 2023. Retrieved 20 February 2024.
- ^ "Regional Agreements Database (United Kingdom)". World Trade Organization. Archived from the original on 25 August 2024.
- ^ Webb, Dominic (16 December 2024). Progress on UK free trade agreement negotiations (PDF). UK Parliament (Report). Archived (PDF) from the original on 24 December 2024. Retrieved 24 December 2024.
- ^ "Isle of Man, Jersey and Guernsey sign deal with UK over post-Brexit trade". BBC News. 26 November 2018. Archived from the original on 16 May 2023. Retrieved 11 December 2023.
- ^ Loft, Philip; Fella, Stefano; Jozepa, Ilze; Mills, Claire; Ward, Matthew (1 August 2022). "Brexit and the UK's Overseas Territories" (PDF). UK Parliament. Archived (PDF) from the original on 3 August 2022. Retrieved 11 December 2023.
- ^ Foster, Peter; Uddin, Rafe; Campbell, Peter (26 January 2024). "UK halts talks with Canada on post-Brexit trade deal". Financial Times. Archived from the original on 26 January 2024. Retrieved 26 January 2024.
