
Back فلمينات Arabic Fulminat Catalan Fulmináty Czech Fulminato Spanish Fulminate French Fulmanáit Irish Fulminati Croatian Fulminat ID Fulminati Italian 雷酸塩 Japanese
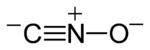 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| 239442 | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| CNO− | |
| Molar mass | 42.018 g·mol−1 |
| Conjugate acid | Fulminic acid |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Fulminates are chemical compounds which include the fulminate ion (CNO−, C−≡N+−O−). The fulminate ion is a pseudohalic ion because its charge and reactivity are similar to those of the halogens. The name is derived from the Latin fulminātus, meaning to explode like lightning, and reflects that fulminate salts are friction-sensitive explosives due to the instability of the ion. The best known is mercury(II) fulminate, which has been used as a primary explosive in detonators. Fulminates can be formed from metals, such as silver and mercury, dissolved in nitric acid, and reacted with ethanol. The weak single nitrogen-oxygen bond is responsible for their instability. Nitrogen very easily forms a stable triple bond to another nitrogen atom, forming nitrogen gas.