
Back Fumaarsuur Afrikaans حمض الفوماريك Arabic فوماریک اسید AZB Fumarna kiselina BS Àcid fumàric Catalan Kyselina fumarová Czech Fumarsyre Danish Fumarsäure German Φουμαρικό οξύ Greek Fumarata acido Esperanto
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(2E)-But-2-enedioic acid | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 605763 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.404 |
| EC Number |
|
| E number | E297 (preservatives) |
| 49855 | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 9126 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H4O4 | |
| Molar mass | 116.072 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Density | 1.635 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 287 °C (549 °F; 560 K) (decomposes)[2] |
| 6.3 g/L at 25 °C[1] | |
| Acidity (pKa) | pka1 = 3.03, pka2 = 4.44 (15 °C, cis isomer) |
| −49.11·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| non zero | |
| Pharmacology | |
| D05AX01 (WHO) | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |

| |
| Warning | |
| H319 | |
| P264, P280, P305+P351+P338, P313 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| 375 °C (707 °F; 648 K) | |
| Related compounds | |
Related carboxylic acids
|
|
Related compounds
|
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
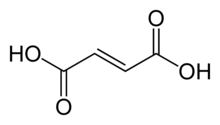
Fumaric acid or trans-butenedioic acid is an organic compound with the formula HO2CCH=CHCO2H. A white solid, fumaric acid occurs widely in nature. It has a fruit-like taste and has been used as a food additive. Its E number is E297.[3] The salts and esters are known as fumarates. Fumarate can also refer to the C
4H
2O2−
4 ion (in solution). Fumaric acid is the trans isomer of butenedioic acid, while maleic acid is the cis isomer.
- ^ Record in the GESTIS Substance Database of the Institute for Occupational Safety and Health
- ^ Pubchem. "Fumaric acid". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.
- ^ Lohbeck, Kurt; Haferkorn, Herbert; Fuhrmann, Werner; Fedtke, Norbert (2000). "Maleic and Fumaric Acids". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. doi:10.1002/14356007.a16_053. ISBN 3-527-30673-0.
