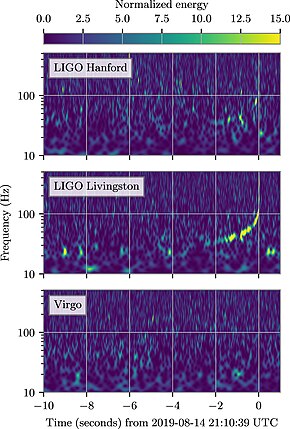
 Time–frequency representations (Chatterji et al. 2004) of data containing GW190814, observed by LIGO Hanford (top), LIGO Livingston (middle), and Virgo (bottom). Times are shown relative to 2019 August 14, 21:10:39 UTC. Each detector's data are whitened by their respective noise amplitude spectral density and a Q-transform is calculated. The colorbar displays the normalized energy reported by the Q-transform at each frequency. These plots are not used in our detection procedure and are for visualization purposes only. | |
| Gravitational wave | |
| Date | 21:10:39 UTC |
|---|---|
| Instrument | LIGO, Virgo[1][2] |
| Right ascension | 03h 33m |
| Declination | 04h 45m |
| Epoch | J2000.0 |
| Distance | 241 megaparsecs (790 Mly)[1] |
| Other designations | GW190814 |
| | |
GW 190814 was a gravitational wave (GW) signal observed by the LIGO and Virgo detectors on 14 August 2019 at 21:10:39 UTC,[2] and having a signal-to-noise ratio of 25 in the three-detector network.[1] The signal was associated with the astronomical super event S190814bv, located 790 million light years away, in location area 18.5 deg2[n 1][1][3][4] towards Cetus or Sculptor.[5][6][7][8][9][10] No optical counterpart was discovered despite an extensive search of the probability region.[11]
- ^ a b c d Cite error: The named reference
AJL-20200623was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Staff (2020). "GW190814 Factsheet - Lowest mass ratio to date - Strongest evidence of higher order modes" (PDF). LIGO. Retrieved 26 June 2020.
- ^ Greco, G.; et al. (2020). "Handling gravitational-wave sky maps for EM-followUP observations - Second ASTERICS Virtual Observatory School" (PDF). Asterics2020.eu. Retrieved 27 June 2020.
- ^ Berry, Christopher (10 August 2018). "Sky-localization of Gravitational wave observations". CplBerry.com. Retrieved 27 June 2020.
- ^ Staff (14 June 2019). "GraceDB - Gravitational-Wave Candidate Event Database - Superevent Info". LIGO. Retrieved 27 June 2020.
- ^ Staff (23 June 2020). "Black hole or neutron star? - LIGO-Virgo scientists find mystery object in 'mass gap'". Pennsylvania State University. Retrieved 24 June 2020.
- ^ Starr, Michelle (16 August 2019). "Early Reports Indicate We May Have Detected a Black Hole And Neutron Star Collision". ScienceAlert.com. Retrieved 16 August 2019.
- ^ Mandelbum, Ryan F. (26 August 2019). "Mystery Deepens Around Newly Detected Ripples in Space-Time". Gizmodo. Retrieved 26 August 2019.
- ^ Starr, Michelle (11 February 2020). "First Papers on The Black Hole-Neutron Star Merger Are In. Here's What We Didn't See". ScienceAlert.com. Retrieved 11 February 2020.
- ^ Ackley, K.; et al. (5 February 2020). "Observational constraints on the optical and near-infrared emission from the neutron star-black hole binary merger S190814bv". arXiv:2002.01950v1 [astro-ph.SR].
- ^ Staff (25 June 2020). "GW190814 Sheds Light on Mass Gap between Neutron Stars and Black Holes". Sci-News.com. Retrieved 26 June 2020.
Cite error: There are <ref group=n> tags on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=n}} template (see the help page).
