
Back Galilea Afrikaans Galiläa ALS Galilea AN Galilēa ANG الجليل (منطقة) Arabic ܓܠܝܠܐ ARC الجليل ARZ Galilea AST Qalileya Azerbaijani الجلیل AZB
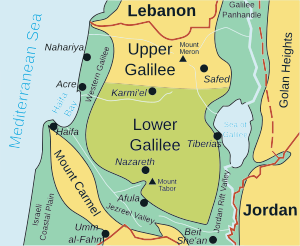
Galilee (/ˈɡælɪliː/;[1] Hebrew: הַגָּלִיל, romanized: hagGālīl; Latin: Galilaea;[2] Arabic: الجليل, romanized: al-Jalīl) is a region located in northern Israel and southern Lebanon consisting of two parts: the Upper Galilee (הגליל העליון, ha-Galil ha-Elyon; الجليل الأعلى, al-Jalīl al-Aʿlā) and the Lower Galilee (גליל תחתון, Galil Taḫton; الجليل الأسفل, al-Jalīl al-Asfal).
Galilee encompasses the area north of the Mount Carmel-Mount Gilboa ridge and south of the east-west section of the Litani River. It extends from the Israeli coastal plain and the shores of the Mediterranean Sea with Acre in the west, to the Jordan Valley to the east; and from the Litani in the north plus a piece bordering on the Golan Heights to Dan at the base of Mount Hermon in the northeast, to Mount Carmel and Mount Gilboa in the south.
It includes the plains of the Jezreel Valley north of Jenin and the Beit She'an Valley, the Sea of Galilee, and the Hula Valley.
- ^ "Galilee". Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary.
- ^ Charlton T. Lewis and Charles Short, A Latin Dictionary, Clarendon Press, Oxford (1879), s.v. Galilaea.