
Back Ykboson Afrikaans Eichboson ALS بوزون عياري Arabic Bosón de gauge AST Калібровачны базон Byelorussian Калибровъчен бозон Bulgarian গেজ বোসন Bengali/Bangla Baždarni bozoni BS Bosó de gauge Catalan Eichboson German
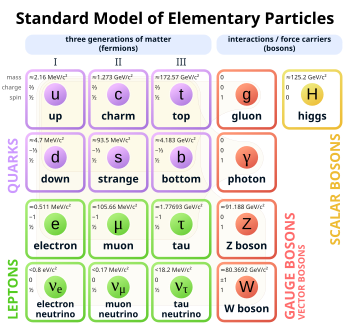
In particle physics, a gauge boson is a bosonic elementary particle that acts as the force carrier for elementary fermions.[1][2] Elementary particles whose interactions are described by a gauge theory interact with each other by the exchange of gauge bosons, usually as virtual particles.
Photons, W and Z bosons, and gluons are gauge bosons. All known gauge bosons have a spin of 1 and therefore are vector bosons. For comparison, the Higgs boson has spin zero and the hypothetical graviton has a spin of 2.
Gauge bosons are different from the other kinds of bosons: first, fundamental scalar bosons (the Higgs boson); second, mesons, which are composite bosons, made of quarks; third, larger composite, non-force-carrying bosons, such as certain atoms.
- ^ Gribbin, John; Gribbin, Mary; Gribbin, Jonathan (2000). Q is for quantum: an encyclopedia of particle physics. New York, New York: Free Press. ISBN 978-0-684-85578-3.
- ^ Clark, John Owen Edward, ed. (2004). The essential dictionary of science. New York: Barnes & Noble Books. ISBN 978-0-7607-4616-5.