
Back قلدانامیسین AZB Geldanamycin German گلدانامیسین Persian Geldanamysiini Finnish Geldanamycine French Geldanamicina Italian Geldanamycyna Polish Geldanamicin Serbo-Croatian Geldanamicin Serbian
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
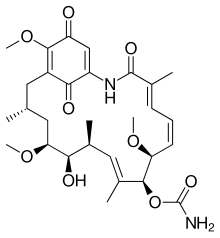
| IUPAC name
(4E,6Z,8S,9S,10E,12S,13R,14S,16R)-13-hydroxy-
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C29H40N2O9 | |
| Molar mass | 560.64 g/mol |
| Appearance | Gold-yellow fine crystalline powder |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Geldanamycin is a 1,4-benzoquinone ansamycin antitumor antibiotic that inhibits the function of Hsp90 (Heat Shock Protein 90) by binding to the unusual ADP/ATP-binding pocket of the protein.[1] HSP90 client proteins play important roles in the regulation of the cell cycle, cell growth, cell survival, apoptosis, angiogenesis and oncogenesis.[2]

Geldanamycin induces the degradation of proteins that are mutated or overexpressed in tumor cells such as v-Src, Bcr-Abl, p53, and ERBB2. This effect is mediated via HSP90. Despite its potent antitumor potential, geldanamycin presents several major drawbacks as a drug candidate such as hepatotoxicity, further, Jilani et al.. reported that geldanamycin induces the apoptosis of erythrocytes under physiological concentrations.[4] These side effects have led to the development of geldanamycin analogues, in particular analogues containing a derivatisation at the 17 position:
- ^ Schulte, T. W.; Akinaga, S.; Soga, S.; Sullivan, W.; Stensgard, B.; Toft, D.; Neckers, L. M. (1998). "Antibiotic radicicol binds to the N-terminal domain of Hsp90 and shares important biologic activities with geldanamycin". Cell Stress & Chaperones. 3 (2): 100–108. doi:10.1379/1466-1268(1998)003<0100:ARBTTN>2.3.CO;2 (inactive 1 November 2024). PMC 312953. PMID 9672245.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of November 2024 (link) - ^ Wayne, N.; Mishra, P.; Bolon, D.N. (2011). "Hsp90 and Client Protein Maturation". Molecular Chaperones. Methods Mol Biol. Vol. 787. pp. 33–44. doi:10.1007/978-1-61779-295-3_3. ISBN 978-1-61779-294-6. PMC 5078872. PMID 21898225.
- ^ Stebbins, C. E.; Russo, A. A.; Schneider, C.; Rosen, N.; Hartl, F. U.; Pavletich, N. P. (1997). "Crystal structure of an Hsp90-geldanamycin complex: Targeting of a protein chaperone by an antitumor agent". Cell. 89 (2): 239–250. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80203-2. PMID 9108479. S2CID 5253110.
- ^ Jilani, Kashif; Qadri, Syed M.; Lang, Florian (2013). "Geldanamycin-Induced Phosphatidylserine Translocation in the Erythrocyte Membrane". Cell Physiol Biochem. 32 (6): 1600–1609. doi:10.1159/000356596. PMID 24335345.