
Back Coğrafi qurşaq Azerbaijani ভৌগোলিক অঞ্চল Bengali/Bangla Zona climàtica Catalan Географин аса CE Geozone German Zonas térmicas Spanish Geograafiline vööde Estonian Zona termiko Basque منطقه جغرافیایی Persian Lämpövyöhyke Finnish
This article needs additional citations for verification. (March 2011) |

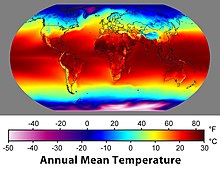
The five main latitude regions of Earth's surface comprise geographical zones,[1] divided by the major circles of latitude. The differences between them relate to climate. They are as follows:
- The North Frigid Zone, between the North Pole at 90° N and the Arctic Circle at 66°33′50.3″ N, covers 4.12% of Earth's surface.
- The North Temperate Zone, between the Arctic Circle at 66°33′50.3″ N and the Tropic of Cancer at 23°26′09.7″ N, covers 25.99% of Earth's surface.
- The Torrid Zone, between the Tropic of Cancer at 23°26′09.7″ N and the Tropic of Capricorn at 23°26′09.7″ S, covers 39.78% of Earth's surface.
- The South Temperate Zone, between the Tropic of Capricorn at 23°26′09.7″ S and the Antarctic Circle at 66°33′50.3″ S, covers 25.99% of Earth's surface.
- The South Frigid Zone, from the Antarctic Circle at 66°33′50.3″ S and the South Pole at 90° S, covers 4.12% of Earth's surface.

Ice cap
Tundra
Boreal
Warm temperate
Subtropical
Tropical
On the basis of latitudinal extent, the globe is divided into three broad heat zones.
- ^ "The Five Geographical Zones Of The World". WorldAtlas. Retrieved 2019-09-17.