
Back جغرافيا فرنسا Arabic Xeografía de Francia AST Fransa coğrafiyası Azerbaijani Геаграфія Францыі Byelorussian Геаграфія Францыі BE-X-OLD География на Франция Bulgarian ফ্রান্সের ভূগোল Bengali/Bangla Geografia de França Catalan Geografie Francie Czech Daearyddiaeth Ffrainc Welsh
This article needs additional citations for verification. (August 2019) |
 | |
| Continent | Europe |
|---|---|
| Region | Western Europe |
| Coordinates | 48°51′N 2°21′E / 48.850°N 2.350°E |
| Area | Ranked 42nd |
| • Total | 643,801 km2 (248,573 sq mi) |
| • Land | 99.48% |
| • Water | 0.52% |
| Coastline | 5,500 km (3,400 mi) |
| Borders | 4,176 km (2,595 mi) |
| Highest point | Mont Blanc 4,808 m (15,774 ft) |
| Lowest point | Étang de Lavalduc −10 m (−33 ft) |
| Longest river | Loire 1,012 km (629 mi) |
| Largest lake | Lac du Bourget 44.5 km2 (17.2 sq mi) |
| Climate | Oceanic climate, Mediterranean climate (south), mountain climate (Alps and Pyrenees) |
| Terrain | Plains and hills (north and west), mountainous (south) |
| Natural resources | Coal, iron ore, bauxite, zinc, uranium, antimony, arsenic, potash, feldspar, fluorspar, gypsum, timber, fish, gold |
| Natural hazards | Flooding, avalanches, midwinter windstorms, drought, forest fires (south) |
| Environmental issues | Water pollution, air pollution, agricultural runoff, acid rain |
| Exclusive economic zone | In Europe: 334,604 km2 (129,191 sq mi) All overseas territories: 11,691,000 km2 (4,514,000 sq mi) |
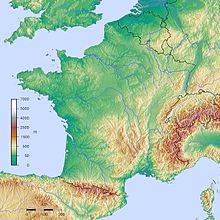

The geography of France consists of a terrain that is mostly flat plains or gently rolling hills in the north and the west and mountainous in the south (including the Massif Central and the Pyrenees) and the east (the country's highest points being in the Alps). Metropolitan France has a total size of 551,695 km2 (213,011 sq mi) (Europe only). It is the third-largest country in Europe by area (after Russia and Ukraine) and the largest in Western Europe.