
Back جغرافيا إيران Arabic Xeografía d'Irán AST İran coğrafiyası Azerbaijani География на Иран Bulgarian ইরানের ভূগোল Bengali/Bangla Geografija Irana BS Geografia de l'Iran Catalan جوگرافیای ئێران CKB Geographie des Iran German Coğrafyay İrani DIQ
  | |
| Continent | Asia |
|---|---|
| Region | West Asia[1][2][3] |
| Coordinates | 32°00'N, 53°00'E |
| Area | Ranked 17th |
| • Total | 1,648,195 km2 (636,372 sq mi) |
| • Land | 99.27% |
| • Water | 0.73% |
| Coastline | 2,815 km (1,749 mi) |
| Borders | Total land borders: 5,894 km (3,662 mi) Afghanistan: 921 km (572 mi) Armenia: 44 km (27 mi) Azerbaijan (proper): 432 km (268 mi) Azerbaijan (Nakhchivan exclave): 179 km (111 mi) Iraq: 1,599 km (994 mi) Pakistan: 909 km (565 mi) Turkey: 534 km (332 mi) Turkmenistan: 1,148 km (713 mi) |
| Highest point | Mount Damavand 5,610 m (18,406 ft) |
| Lowest point | Caspian Sea −28 m (−91.9 ft) |
| Longest river | Karun |
| Largest lake | Lake Urmia |
| Exclusive economic zone | 168,718 km2 (65,142 sq mi) |
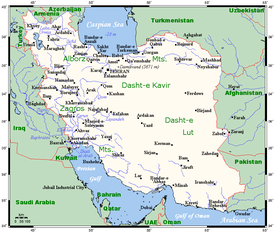
Geographically, the country of Iran is located in West Asia and the bodies of water the nation borders are the Caspian Sea, Persian Gulf (Arabian Gulf), and Gulf of Oman. Topographically, it is predominantly located on the Iranian/Persian plateau, Its mountains have impacted both the political and the economic history of the country for several centuries. The mountains enclose several broad basins, on which major agricultural and urban settlements are located. Until the 20th century, when major highways and railroads were constructed through the mountains to connect the population centers, these basins tended to be relatively isolated from one another.


Typically, one major town has dominated each basin, and there were complex economic relationships between the town and the hundreds of villages that surrounded it. In the higher elevations of the mountains rimming the basins, tribally organized groups practiced transhumance, moving with their herds of sheep and goats between traditionally established summer and winter pastures. There are no major river systems in the country, and historically transportation was by means of caravans that followed routes traversing gaps and passes in the mountains. The mountains also impeded easy access to the Persian Gulf and the Caspian Sea.
With an area of 1,648,195 square kilometres (636,372 sq mi), Iran ranks seventeenth in size among the countries of the world. Iran shares its northern borders with several post-Soviet states: Armenia, Azerbaijan,[a] and Turkmenistan. These borders extend for more than 2,000 kilometres (1,200 mi), including nearly 650 kilometres (400 mi) of water along the southern shore of the Caspian Sea. Iran's western borders are with Turkey in the north and Iraq in the south, terminating at the Arvand Rud.
The Persian Gulf and Gulf of Oman littorals form the entire 1,770-kilometre (1,100 mi) southern border. To the east lie Afghanistan on the north and Pakistan on the far south. Iran's diagonal distance from Azerbaijan in the northwest to Sistan and Baluchestan province in the southeast is approximately 2,333 kilometres (1,450 mi).
- ^ "Iran Country Profile". BBC News. 16 August 2011. Archived from the original on 25 November 2014. Retrieved 26 November 2014.
- ^ ""CESWW" – Definition of Central Eurasia". Cesww.fas.harvard.edu. Archived from the original on 5 August 2010. Retrieved 26 November 2014.
- ^ "Iran Guide". National Geographic. 14 June 2013. Archived from the original on 12 December 2009. Retrieved 26 November 2014.
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).