
Back Albanés gheg AST Албан теленең гег диалекты Bashkir Гегскі дыялект албанскай мовы Byelorussian Гескі дыялект альбанскай мовы BE-X-OLD Геги Bulgarian Gegština Czech Geg Welsh Gegisch German Γκεγκική διάλεκτος Greek Geg-albana lingvo Esperanto
| Gheg | |
|---|---|
| gegnisht | |
| Region | Albania, Kosovo, North Macedonia, Montenegro, Serbia |
Native speakers | 4.1 million (2012–2021)[1] |
Early form | |
| Dialects | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | aln |
| Glottolog | gheg1238 |
| Linguasphere | 55-AAA-aa |
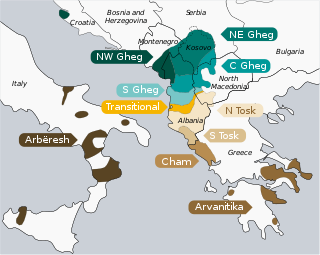 A map showing Gheg speakers in green. | |
Gheg or Geg (Gheg Albanian: gegnisht, Standard Albanian: gegërisht) is one of the two major varieties of Albanian, the other being Tosk. The geographic dividing line between the two varieties is the Shkumbin River, which winds its way through central Albania.[2][3] Gheg is spoken in northern and central Albania, Kosovo, northwestern North Macedonia, southeastern Montenegro and southern Serbia by the Albanian dialectal subgroup known as Ghegs.[3]
Gheg does not have any official status as a written language in any country. Publications in Kosovo and North Macedonia are in Standard Albanian, which is based on Tosk. However, some authors continue to write in Gheg.
- ^ Gheg at Ethnologue (25th ed., 2022)

- ^ Brown and Ogilvie (2008), p. 23. The river Shkumbin in central Albania historically forms the boundary between those two dialects, with the population on the north speaking varieties of Geg and the population on the south varieties of Tosk.
- ^ a b Joseph 2003, When Languages Collide: Perspectives on Language Conflict, Language Competition, and Language Coexistence, p. 266: "Northeastern Geg"