
Back حمض الغلوكورونيك Arabic اسید قلوکورونیک AZB Глюкуронова киселина Bulgarian Glukuronska kiselina BS Àcid glucurònic Catalan Kyselina glukuronová Czech Glucuronsäure German Glukuronata acido Esperanto Ácido glucurónico Spanish Glükuroonhape Estonian
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
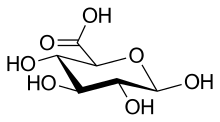
| IUPAC name
β-D-Glucopyranuronic acid
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(2S,3S,4S,5R,6R)-3,4,5,6-Tetrahydroxyoxane-2-carboxylic acid | |
| Other names
β-D-Glucuronic acid, GlcA
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.026.807 |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | Glucuronic+acid |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H10O7 | |
| Molar mass | 194.139 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 159 to 161 °C (318 to 322 °F; 432 to 434 K)[1] |
| Related compounds | |
Related uronic acids
|
Alluronic acid, Altruronic acid, Arabinuronic acid, Fructuronic acid, Galacturonic acid, Guluronic acid, Iduronic acid, Lyxuronic acid, Mannuronic acid, Psicuronic acid, Riburonic acid, Ribuluronic acid, Sorburonic acid, Tagaturonic acid, Taluronic acid, Xyluluronic acid, Xyluronic acid |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Glucuronic acid (GCA, from Ancient Greek: γλεῦκος + οὖρον, lit. 'sweet wine, must + urine') is a uronic acid that was first isolated from urine (hence the name "uronic acid"). It is found in many gums such as gum arabic (approx. 18%), xanthan, and kombucha tea and is important for the metabolism of microorganisms, plants and animals.