
Back جلسيروفوسفوليبيد Arabic Fosfoglicèrid Catalan Glycerolfosfolipid Czech Glycerofosfolipid Danish Phosphoglyceride German Fosfoglicérido Spanish Fosfoglizerido Basque Phosphoglycéride French Fosfoglicérido Galician פוספוגליצריד HE
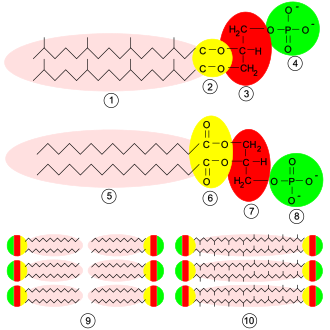
Glycerophospholipids or phosphoglycerides are glycerol-based phospholipids. They are the main component of biological membranes in eukaryotic cells. They are a type of lipid, of which its composition affects membrane structure and properties.[1] Two major classes are known: those for bacteria and eukaryotes and a separate family for archaea.[2]
- ^ Harayama, Takeshi; Riezman, Howard (May 2018). "Understanding the diversity of membrane lipid composition". Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology. 19 (5): 281–296. doi:10.1038/nrm.2017.138. ISSN 1471-0080. PMID 29410529.
- ^ Caforio, Antonella; Driessen, Arnold J.M. (2017). "Archaeal phospholipids: Structural properties and biosynthesis" (PDF). Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids. 1862 (11): 1325–1339. doi:10.1016/j.bbalip.2016.12.006. PMID 28007654.