Back Бырзентәыла Abkhazian Yunani ACE Урымые ADY Griekeland Afrikaans Griechenland ALS ግሪክ (አገር) Amharic Greece AMI Grecia AN Grecland ANG Giris ANN
Hellenic Republic | |
|---|---|
| Motto: Ελευθερία ή Θάνατος Elefthería í Thánatos (English: "Freedom or Death") | |
| Anthem: Ύμνος εις την Ελευθερίαν Ímnos is tin Eleftherían (English: "Hymn to Liberty") | |
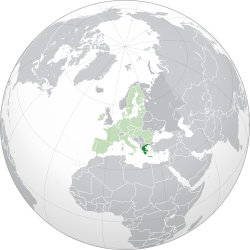
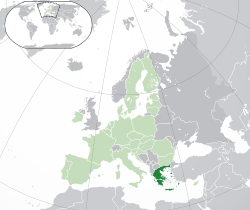
Location of Greece (dark green) – in Europe (light green & dark grey) | |
| Capital and largest city | Athens 37°58′N 23°43′E / 37.967°N 23.717°E |
| Official language and national language | Greek |
| Religion (2017) |
|
| Demonym(s) |
|
| Government | Unitary parliamentary republic |
| Katerina Sakellaropoulou | |
| Kyriakos Mitsotakis | |
| Vacant | |
| Legislature | Hellenic Parliament |
| Establishment history | |
• Greek War of Independence against the Ottoman Empire | 25 March 1821 (traditional starting date) |
| 1 January 1822 | |
| 3 February 1830 | |
| 24 July 1974 | |
| 11 June 1975 | |
| Area | |
• Total | 131,957 km2 (50,949 sq mi)[3] (95th) |
• Water (%) | 1.51 (2015)[2] |
| Population | |
• 2024 estimate | |
• 2021 census | |
• Density | 78.9/km2 (204.4/sq mi) (105th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2024 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| GDP (nominal) | 2024 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| Gini (2023) | medium inequality |
| HDI (2022) | very high (33rd) |
| Currency | Euro (€) (EUR) |
| Time zone | UTC+02:00 (EET) |
• Summer (DST) | UTC+03:00 (EEST) |
| Date format | dd.mm.yyyy (AD)b |
| Drives on | Right |
| Calling code | +30 |
| ISO 3166 code | GR |
| Internet TLD | |
| |
Greece,[a] officially the Hellenic Republic,[b] is a country in Southeast Europe. Located on the southern tip of the Balkan peninsula, Greece shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to the east. The Aegean Sea lies to the east of the mainland, the Ionian Sea to the west, and the Sea of Crete and the Mediterranean Sea to the south. Greece has the longest coastline on the Mediterranean Basin, featuring thousands of islands. The country comprises nine traditional geographic regions, and has a population of over 10.4 million. Athens is the nation's capital and largest city, followed by Thessaloniki and Patras.
Greece is considered the cradle of Western civilisation, being the birthplace of democracy, Western philosophy, Western literature, historiography, political science, major scientific and mathematical principles, theatre, and the Olympic Games. From the eighth century BC, the Greeks were organised into various independent city-states known as poleis (singular polis) that spanned the Mediterranean and Black seas. Philip II of Macedon united most of present-day Greece in the fourth century BC, with his son Alexander the Great rapidly conquering much of the known ancient world from the eastern Mediterranean to northwestern India. The subsequent Hellenistic period saw the height of Greek culture and influence in antiquity. Greece was annexed by Rome in the second century BC, becoming an integral part of the Roman Empire and its continuation, the Byzantine Empire, which was predominately Greek in culture and language. The Greek Orthodox Church, which emerged in the first century AD, helped shape modern Greek identity and transmitted Greek traditions to the wider Orthodox world. After the Fourth Crusade in 1204, Latin possessions were established in parts of the Greek peninsula, but most of the area fell under Ottoman rule by the mid-15th century.
Following a protracted war of independence, which started in 1821, Greece emerged as a modern nation state in 1830. Over the first hundred years, the Kingdom of Greece sought territorial expansion, which was mainly realised in the early 20th century during the Balkan Wars and up until the catastrophic defeat of its Asia Minor Campaign in 1922. The short-lived republic that was established in 1924 was beset by the ramifications of civil strife and the challenge of resettling refugees from Turkey. In 1936 a royalist dictatorship inaugurated a long period of authoritarian rule, marked by military occupation, civil war and military dictatorship. Greece transitioned to democracy in 1974–75, leading to the current parliamentary republic.
Having achieved record economic growth from 1950 through the 1970s, Greece is a developed country with an advanced high-income economy. A founding member of the United Nations, Greece was the tenth member to join what is today the European Union in 1981 and is part of the eurozone. It is a member of other international institutions, including the Council of Europe, NATO (since 1952), the OECD, the WTO, and the OSCE. Greece has a unique cultural heritage, large tourism industry, and prominent shipping sector. The country's rich historical legacy is reflected in part by its 19 UNESCO World Heritage Sites. Greece was the ninth most-visited country in the world in 2023.
- ^ "Religious Belief and National Belonging in Central and Eastern Europe". Pew Research Center. 10 May 2017. Archived from the original on 24 February 2018. Retrieved 9 September 2017.
- ^ "Surface water and surface water change". Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). Archived from the original on 24 March 2021. Retrieved 11 October 2020.
- ^ "Country Comparison: Area". The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. Archived from the original on 13 November 2020. Retrieved 7 January 2013.
- ^ "Estimated Population and Migration Flows, 2024". Piraeus: Hellenic Statistical Authority. 31 December 2024. Retrieved 8 January 2025.
- ^ Αποτελέσματα Απογραφής Πληθυσμού - Κατοικιών 2021 [Results of Population-Housing Census 2021] (in Greek). Piraeus: Hellenic Statistical Authority. 19 July 2022. Archived from the original on 6 June 2023. Retrieved 8 January 2024.
- ^ a b c d "World Economic Outlook Database, October 2024 Edition. (Greece)". www.imf.org. International Monetary Fund. 22 October 2024. Retrieved 29 November 2024.
- ^ "Income inequality, 2023". Piraeus: Hellenic Statistical Authority. 3 April 2024. Retrieved 3 April 2024.
- ^ "Human Development Report 2023/24" (PDF). United Nations Development Programme. 13 March 2024. Archived (PDF) from the original on 13 March 2024. Retrieved 13 March 2024.
- ^ "The Constitution of Greece: Section II Relations of Church and State: Article 3". Archived from the original on 2 October 2017. Hellenic Resources network
- ^ Enyedi, Zsolt; Madeley, John T.S. (2 August 2004). Church and State in Contemporary Europe. Routledge. p. 228. ISBN 9781135761417.
Both as a state church and as a national church, the Orthodox Church of Greece has a lot in common with Protestant state churches, and even with Catholicism in some countries.
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).