
Back هيبتامينول Arabic هپتامینول AZB Heptaminol Czech Heptaminol German Heptaminol Spanish هپتامینول Persian Heptaminol French Heptaminol Hungarian Heptaminol Portuguese Heptaminol Serbo-Croatian
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
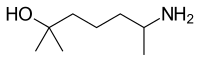
| IUPAC name
(RS)-6-Amino-2-methylheptan-2-ol
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.144 |
| EC Number |
|
| MeSH | Heptaminol |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H19NO | |
| Molar mass | 145.246 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 0.895 g/mL |
| Boiling point | 250 °C (482 °F; 523 K) |
| Pharmacology | |
| C01DX08 (WHO) | |
| Oral, intravenous, intramuscular | |
| Pharmacokinetics: | |
| Renal | |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
Corrosive |
| GHS labelling: | |
 
| |
| Danger | |
| H314, H315, H319, H335 | |
| P260, P261, P264, P271, P280, P301+P330+P331, P302+P352, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P312, P321, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P363, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
| Flash point | 105 °C (221 °F; 378 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Heptaminol is an amino alcohol which is classified as a cardiac stimulant (positive inotropic action). It also increases coronary blood flow along with mild peripheral vasoconstriction. It is sometimes used in the treatment of low blood pressure, particularly orthostatic hypotension as it is a potent positive inotrope (improving cardiac contraction).[medical citation needed]